
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Mathematics
Quarter 3 – Module 7:
Trapezoids and Kite

Mathematics – Grade 9
Alternative Delivery Mode
Quarter 3 – Module 8: Trapezoids and Kite
First Edition, 2020
Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work
of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or
office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit.
Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of
royalties.
Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names,
trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders.
Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from
their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim
ownership over them.
Published by the Department of Education
Secretary: Leonor Magtolis Briones
Undersecretary: Diosdado M. San Antonio
Printed in the Philippines by ________________________
Department of Education - National Capital Region
Office Address: Misamis St., Brgy. Bago Bantay, Quezon City
Telefax: (632) 8926-2213 /8929-4330 /8920-1490 and 8929-4348
E-mail Address: [email protected]ov.ph
Development Team of the Module
Writer: Marisel S. Taduran
Editors: Corazon T. Misa, Cristina R. Solis, Catherine C. De Guzman
Reviewers: Remylinda T. Soriano, Angelita Z. Modesto, George B. Borromeo
Layout Artist: Pepe M. Tabanao, Jr.
Management Team: Malcolm S. Garma, Genia V. Santos, Dennis M. Mendoza
Maria Magdalena M. Lim, Aida H. Rondilla, Lucky S. Carpio

9
Mathematics
Quarter 3 – Module 7:
Trapezoids and Kite
Introductory Message
This Self-Learning Module (SLM) is prepared so that you, our dear learners,
can continue your studies and learn while at home. Activities, questions, directions,
exercises, and discussions are carefully stated for you to understand each lesson.
Each SLM is composed of different parts. Each part shall guide you step-by-
step as you discover and understand the lesson prepared for you.
Pre-tests are provided to measure your prior knowledge on lessons in each
SLM. This will tell you if you need to proceed on completing this module or if you
need to ask your facilitator or your teacher’s assistance for better understanding of
the lesson. At the end of each module, you need to answer the post-test to self-check
your learning. Answer keys are provided for each activity and test. We trust that you
will be honest in using these.
In addition to the material in the main text, Notes to the Teacher are also
provided to our facilitators and parents for strategies and reminders on how they can
best help you on your home-based learning.
Please use this module with care. Do not put unnecessary marks on any part
of this SLM. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises and tests. And
read the instructions carefully before performing each task.
If you have any questions in using this SLM or any difficulty in answering the
tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator.
Thank you.

1
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
What I Need to Know
LEARNING COMPETENCY
The learners will be able to:
Prove theorems on Trapezoid and kite
Solve problems involving Trapezoid and kite (M9GE – IIId – 2)
What I Know
Let see how much knowledge you have about the module. Answer and write
the letter that you think is the best answer to each question on a sheet of paper.
Answer all items.
1. A trapezoid have ______ sides.
a.) 2 b.) 3 c.) 4 d.) 5
2. The mid-segment of a trapezoid connects the midpoints of the ______.
a.) bases b.) legs c.) leg and base d.) base and leg
3. The two parallel sides of a trapezoid are called ______?
a.) legs b.) bases c.) altitudes d.) sides
4. Which of the following is NOT considered a type of trapezoid?
a.) scalene trapezoid c.) right trapezoid
b.) obtuse trapezoid d.) isosceles trapezoid
5. Find the median of a trapezoid with bases of lengths 9 cm and 7 cm.
a.) 8 cm b.) 9 cm c.) 10 cm d.) 11 cm
6. Which of the following has congruent diagonals?
a.) Scalene trapezoid c.) Kite
b.) Right Trapezoid d.) Isosceles trapezoid
2
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
7. Which of the following quadrilaterals has diagonals that do not bisect each other.
a.) Rhombus c.) Isosceles Trapezoid
b.) Square d.) Rectangle
8. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a.) A trapezoid has four congruent sides.
b.) A trapezoid can have three right angles.
c.) Base angles of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent.
d.) The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid bisect each other.
9. An isosceles trapezoid shares some common properties with which triangle?
a.) Equilateral triangle c.) Acute triangle
b.) Isosceles triangle d.) Obtuse triangle
10. Which of the following statements about isosceles trapezoid is TRUE?
a.) Opposite angles are complementary.
b.) Opposite angles are congruent.
c.) Diagonals are congruent.
d.) All sides are congruent.
3
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Lesson
1
TRAPEZOIDS AND KITE
In the previous topic, you have learned about midline theorem. You were able
to write the proof for midline theorem and solve problems involving midline theorem.
This module will help you understand more on trapezoid and kite.
What’s In
Activity No. 1: Hide and Seek
Look around the corner and give or create an example of a trapezoid, and a
kite that can be seen inside your house; using a ruler and protractor, measure its
sides and angles and draw to show that it is a trapezoid, and a kite.
Example:
What’s New
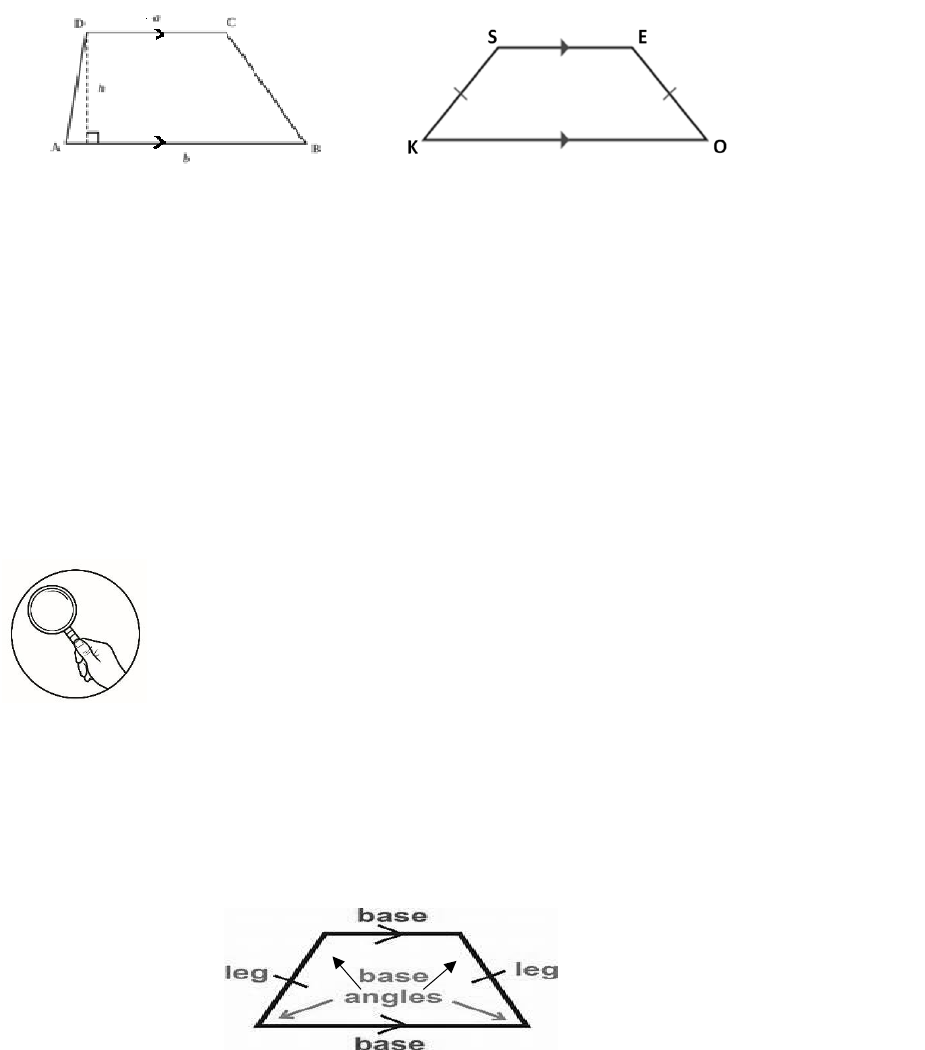
Activity 2
“Mathematical Investigation”
In this activity, the students will think, explore, and give the definition based on
the given figure.
4
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Figure # 1 Figure # 2
Guide questions (Verify your answers using the markings on the figures).
1. In figure #1, which sides are the bases? Why do we say that these sides are the
bases?
2. In figure #1, which sides are the legs? Why do we say that these sides are the
legs?
3. In figure #2, which sides are the bases? Why do we say that these sides are the
bases?
4. In figure #2, which sides are the legs? Why do we say that these sides are the
legs?
What do you notice from figure 1 and figure 2?
What is It
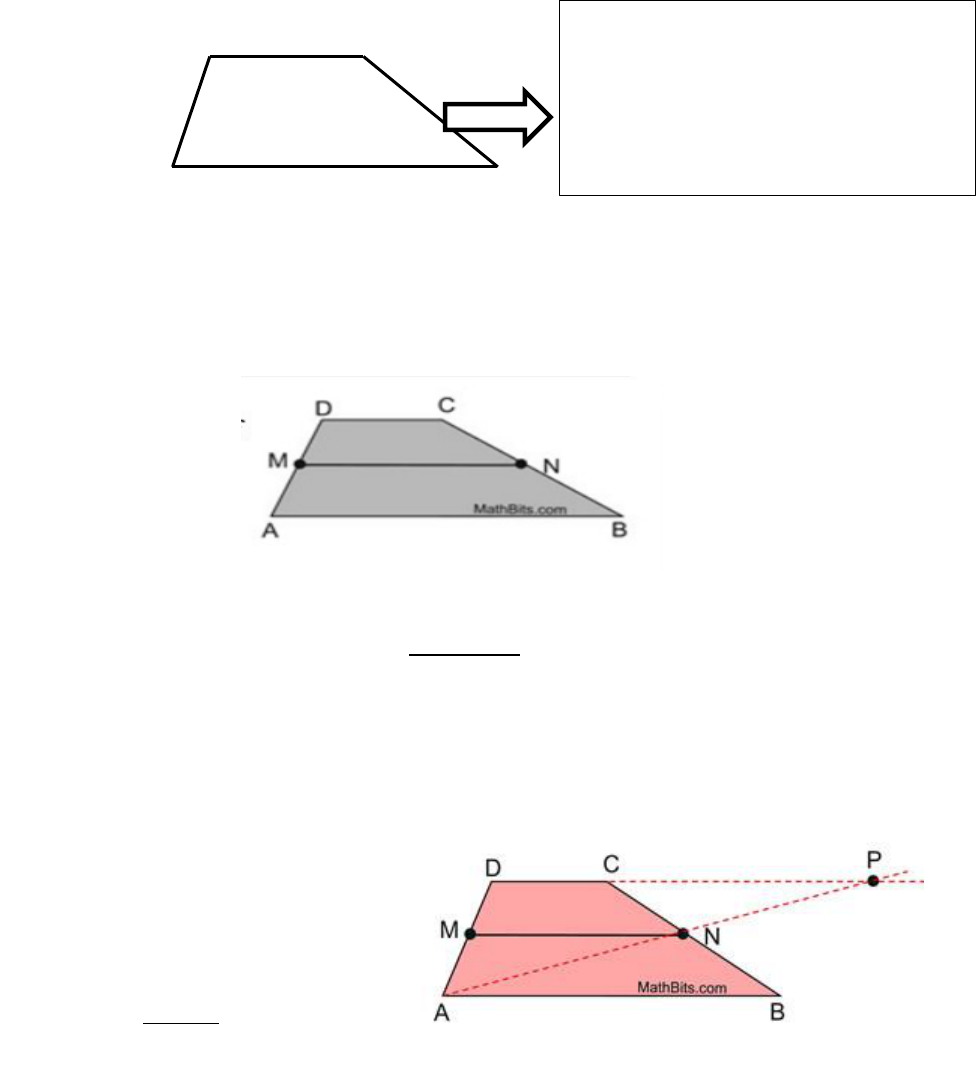
1. Trapezoid is a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides.
The parallel sides are called bases.
The non-parallel sides are called legs.
The base angles of a trapezoid are consecutive angles whose common side is a
base of the trapezoid.
Trapezoids have two pairs of base angles.
5
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
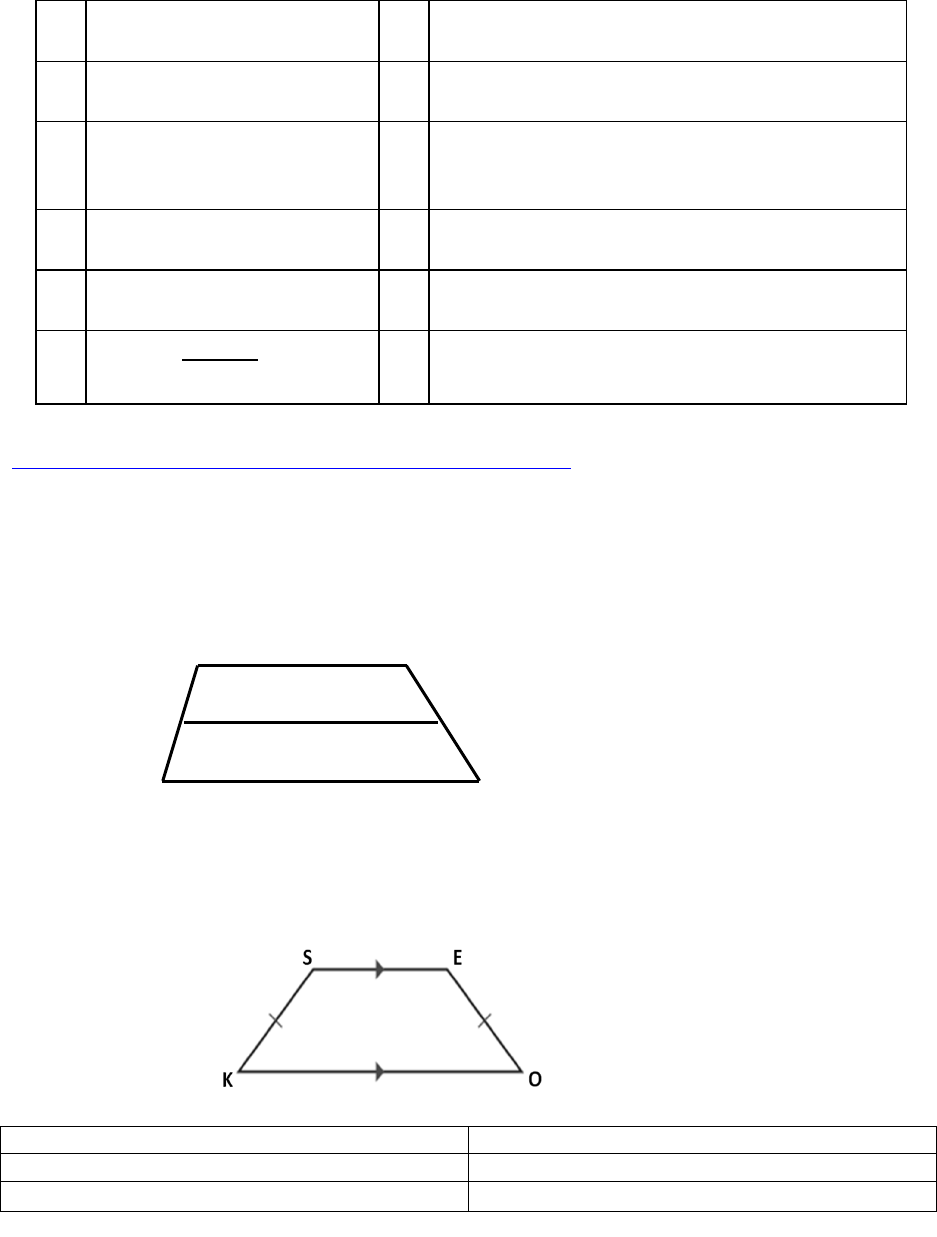
Example
The median of a trapezoid is a segment joining the midpoints of the legs of
the trapezoid.
Theorem
The median of a trapezoid is parallel to the bases and the length of which is equal to half the
sum of the lengths of the bases.
In trapezoid ABCD,
is the median. Length of the median = ½ (length of the upper base +
length of the lower base)
Given: Trapezoid ABCD
Median
Prove:
||
;
||
, and
W A
M R
Legs
and
Bases
and
Lower Base Angles:
WMR and ARM
Upper Base Angles:
MWA and RAW
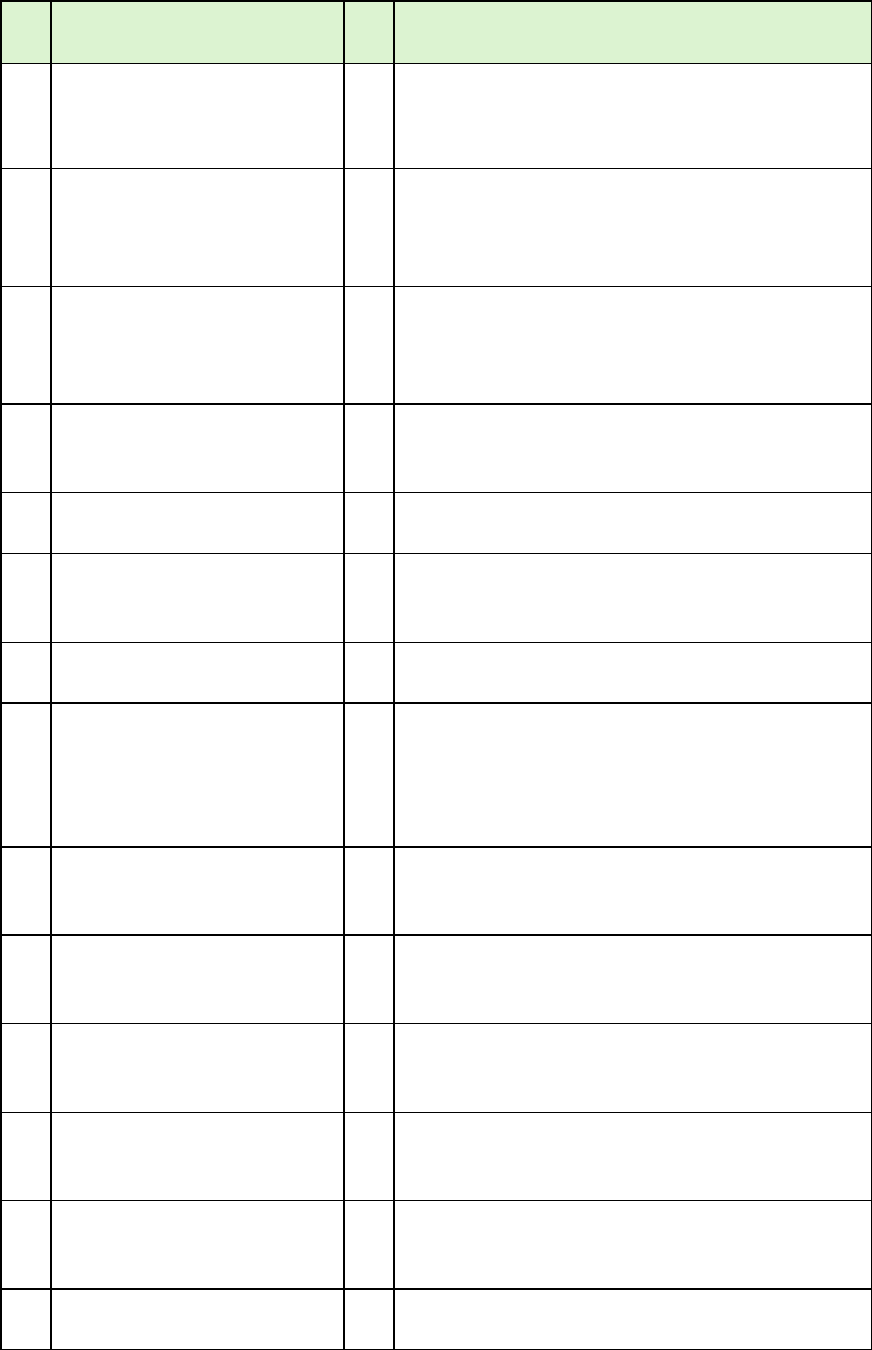
6
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Proof:
Statements
Reasons
1.
Trapezoid ABCD
is the median
1.
Given
2.
Draw
, extending until
it intersects with the
extension of
, at P.
2.
Two points determine exactly one line.
3.
N is the midpoint of
.
M is the midpoint of
.
3.
A median of a trapezoid joins the
midpoints of the legs.
4.
.
4.
Midpoint of a segment divides the segment
into two congruent segments.
5.
.
5.
Bases of a trapezoid are parallel.
6.
ABN
PCN
6.
If 2 || lines are cut by a transversal, then
the alternate interior s are congruent.
7.
ANB
PNC
7.
Vertical s are congruent.
8.
8.
ASA postulate: If 2 s and the included
side of one Δ are congruent to the
corresponding parts of another Δ, then the
Δs are congruent.
9.
9.
CPCTC-corresponding parts congruent Δs
are congruent.
10.
N is midpoint of
.
10.
Midpoint of a segment divides the segment
into two congruent segments.
11.
is the mid-segment of
ΔADP.
11.
Mid-segment of a Δ joins the midpoints of
two sides of the Δ.
12.
(
)*
12.
Mid-segment of Δ is parallel to the third
side of the Δ.
13.
13.
If 2 lines are || to the same line, then they
are || to each other.
14.
|MN| = ½ |DP| or
14.
The length of the mid-segment of a Δ is
7
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
(2|MN| = |DP|)
one-half of the length of the third side.
15.
|DP| = |CP| + |DC|
15.
Segment Addition Postulate
16.
|AB| = |CP|
16.
Congruent segments have equal length
(#9).
17.
|DP| = |AB| + |DC|
17.
Substitution
18.
2|MN| = |AB| + |DC|
18.
Substitution
19.
|MN| =
19.
Division
https://mathbitsnotebook.com/Geometry/Quadrilaterals/QDTrapKite.html#
Example: Given trapezoid NICE below, find |AB|.
N 12 cm I
| AB| = ½ (|NI| + |EC|)
|AB| = ½ (12 + 16)
16 cm |AB| = ½ (28)
|AB| = 14 cm
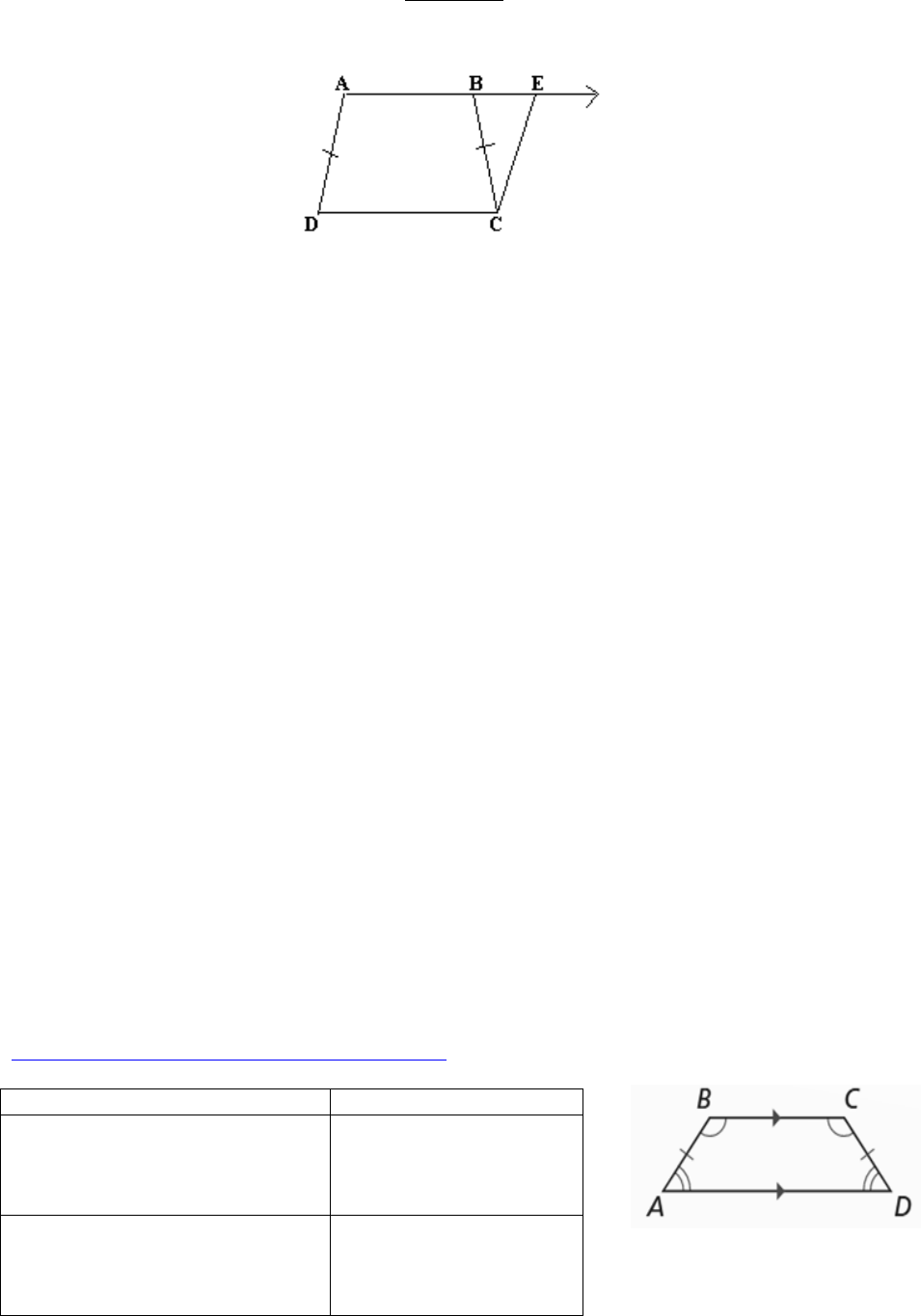
1.1 An isosceles trapezoid is a trapezoid whose nonparallel sides are
congruent.
If the legs of a trapezoid are congruent, then the trapezoid is an isosceles
trapezoid.
Property
Illustration/Example
1. The bases are parallel.
2. The legs are congruent.
E
C
A
B
8
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Theorem
If a trapezoid is isosceles, then each pair of base angles are congruent.
Given: ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid.
and
||
.
Prove that: C D and A B
Proof:
Statements
Reasons
1) ABCD is a trapezoid.
1) Given
2)
||
2) Given
3)
3) Given
4)
||
4) By construction
5) ADCE is a parallelogram.
5) By Properties of parallelogram.
6)
and
6) By properties of parallelogram.
7)
7)
and
(Transitive
property)
8) CEB CBE
8) If
then angles opposite to
them are congruent.
9) DAB ABC
9) Property of parallelogram and
linear pair angles
10) mA + mD =
and
mB + mC =
10) Interior angles on the same side
of the transversal are
supplementary.
11) mA + mD = mC + mB
11) Transitivity (Right sides are same
so left sides are equal).
12) D C
12) From #9 above (A B)
https://www.ask-math.com/trapezoid-and-its-theorems.html
Property
Illustration/Example
3. The lower base angles
of an isosceles
trapezoid are
congruent.
BAD CDA
4. The upper base angles
of an isosceles
trapezoid are
congruent.
ABC DCB
9
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Theorem
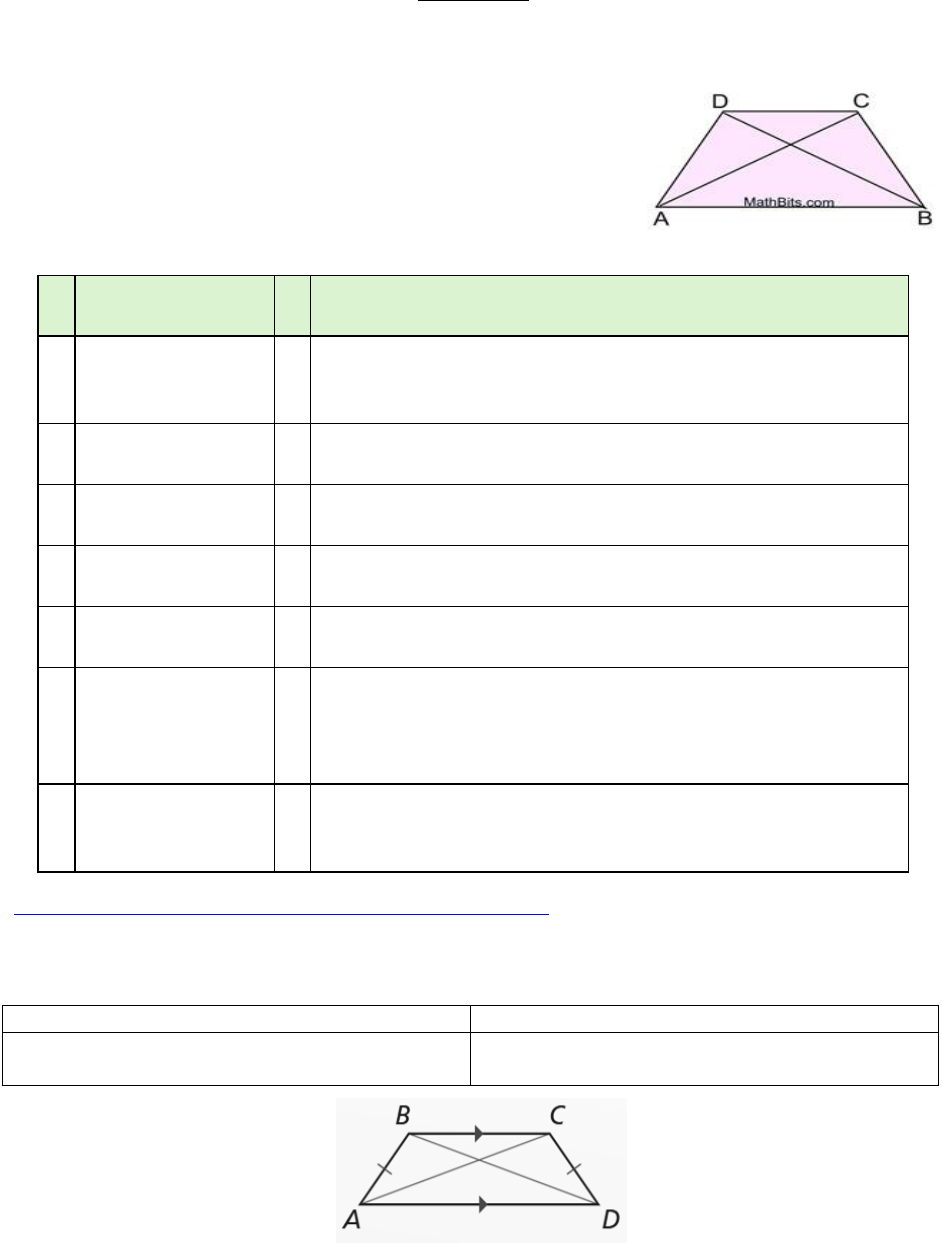
If a quadrilateral is an isosceles trapezoid, then the diagonals are congruent.
If a quadrilateral is an isosceles trapezoid, then the diagonals are
congruent.
Given: Isosceles Trapezoid ABCD
Prove:
Statements
Reasons
1.
Isosceles
Trapezoid ABCD
1.
Given
2.
DAB
CBA
2.
Base angles of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent.
3.
||
3.
Bases of a trapezoid are parallel.
4.
4.
An isos. trap. has congruent legs.
5.
5.
Reflexive property.
6.
ΔDAB ΔCBA
6.
SAS postulate: If 2 sides and the included
of one Δ
are congruent to the corresponding parts of another
Δ, then the Δs are congruent.
7.
7.
CPCTC: Corresponding parts of congruent Δs are
congruent
https://mathbitsnotebook.com/Geometry/Quadrilaterals/ThIsos2Pf.html
Property
Illustration/Example
5. The diagonals of an isosceles
trapezoid are congruent.
10
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
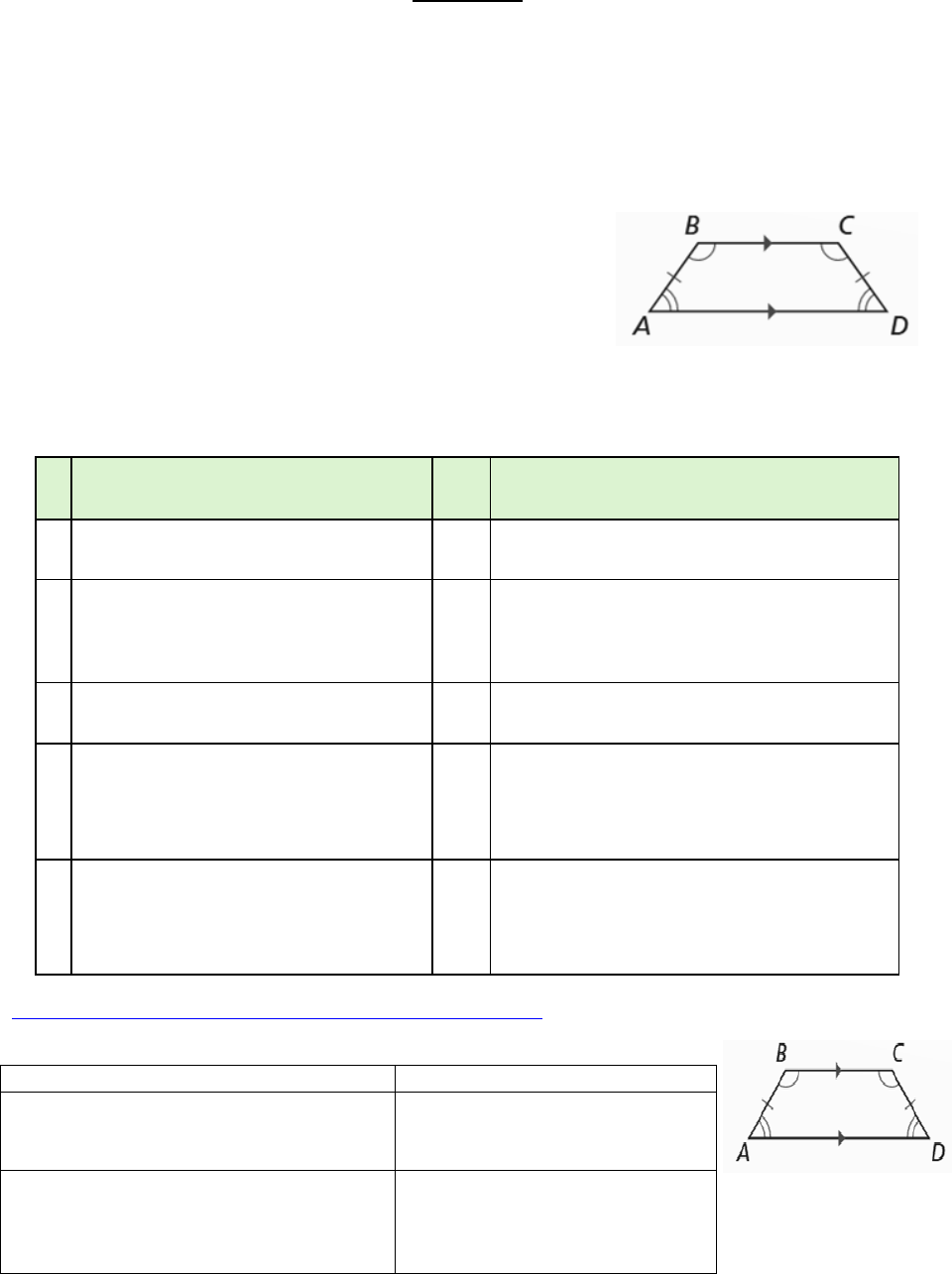
Theorem
If a quadrilateral is an isosceles trapezoid, then the opposite angles are
supplementary.
If a quadrilateral is an isosceles trapezoid, then the opposite angles
are supplementary.
Given: Isosceles Trapezoid ABCD
Prove: A and C are supplementary
and
B and D are supplementary.
Proof:
Statements
Reasons
1.
Isosceles trapezoid ABCD
1.
Given
2.
D
A
B
C
2.
Base angles of an isosceles trapezoid
are congruent.
3.
||
3.
Bases of a trapezoid are parallel.
4.
D and C are supplementary,
and
A and B are supplementary.
4.
If 2 || lines are cut by a transversal,
the interior s on the same side of
transversal are supplementary.
5.
A and C are supplementary,
and
D and B are supplementary.
5.
Substitution
https://mathbitsnotebook.com/Geometry/Quadrilaterals/ThIsos3Pf.html
Property
Illustration/Example
6. The opposite angles of an
isosceles trapezoid are
supplementary.
A and C are supplementary,
and
D and B are supplementary.
7. Any lower base angle of an
isosceles trapezoid is
supplementary to any upper
base angle.
mA mB = 180
mD mC = 180
mA mC = 180
mD mB = 180
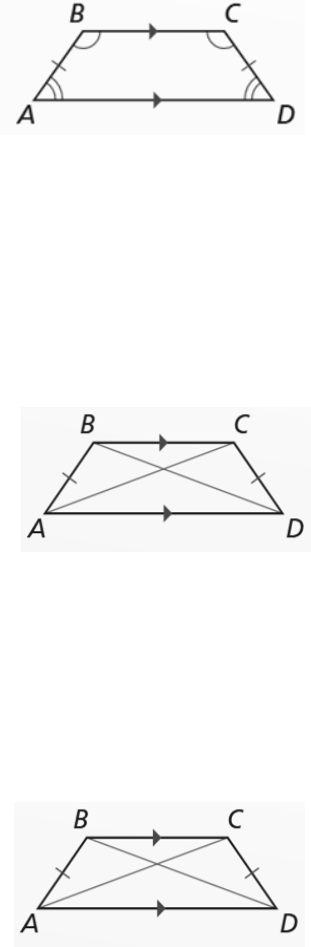
11
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Let us apply the different properties of the trapezoid in solving the following exercises.
Example 1: In the figure below, ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid. Find the measure of angle C if mD
= 70.
Solution: In an isosceles trapezoid, any lower base angle is supplementary to any upper
base angle. Thus,
mC mD = 180
mC 70 = 180
mC = 180 - 70
mC = 110
Example 2: In the figure below, ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid. Find the length of
if |BD| = 9 cm.
Solution: The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent,
.
Thus, |AC| = |BD|
|AC| = 9 cm
Example 3: In the figure below, ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid. Find the value of x if length of
if |AC| = 5x - 30 cm ad |BD|= 60 cm.
Solution: The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent,
.
Thus, |AC| = |BD|
12
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
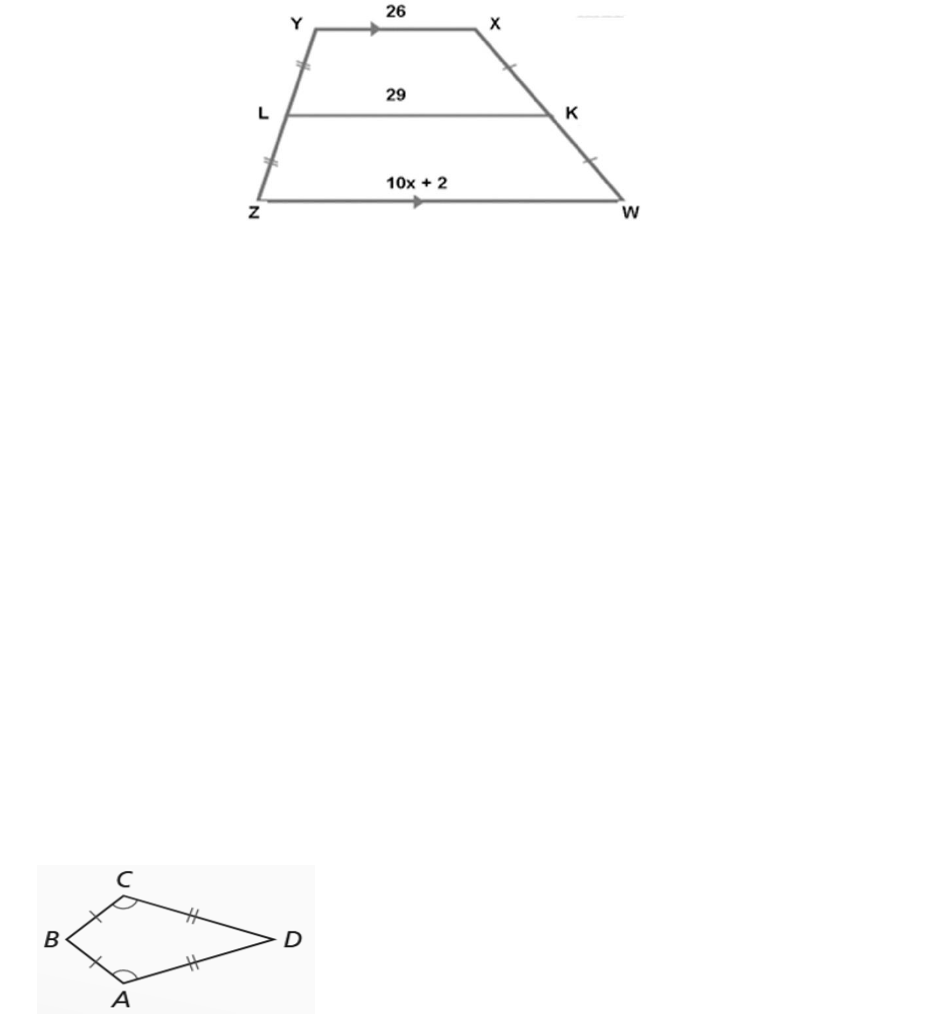
Example 4: In the figure below, YXWZ is a trapezoid. Find the length of
.
Solution: The median (midsegment) of a trapezoid measures one-half the sum of the
lengths of the bases.
Therefore,
; then
|ZW|
units
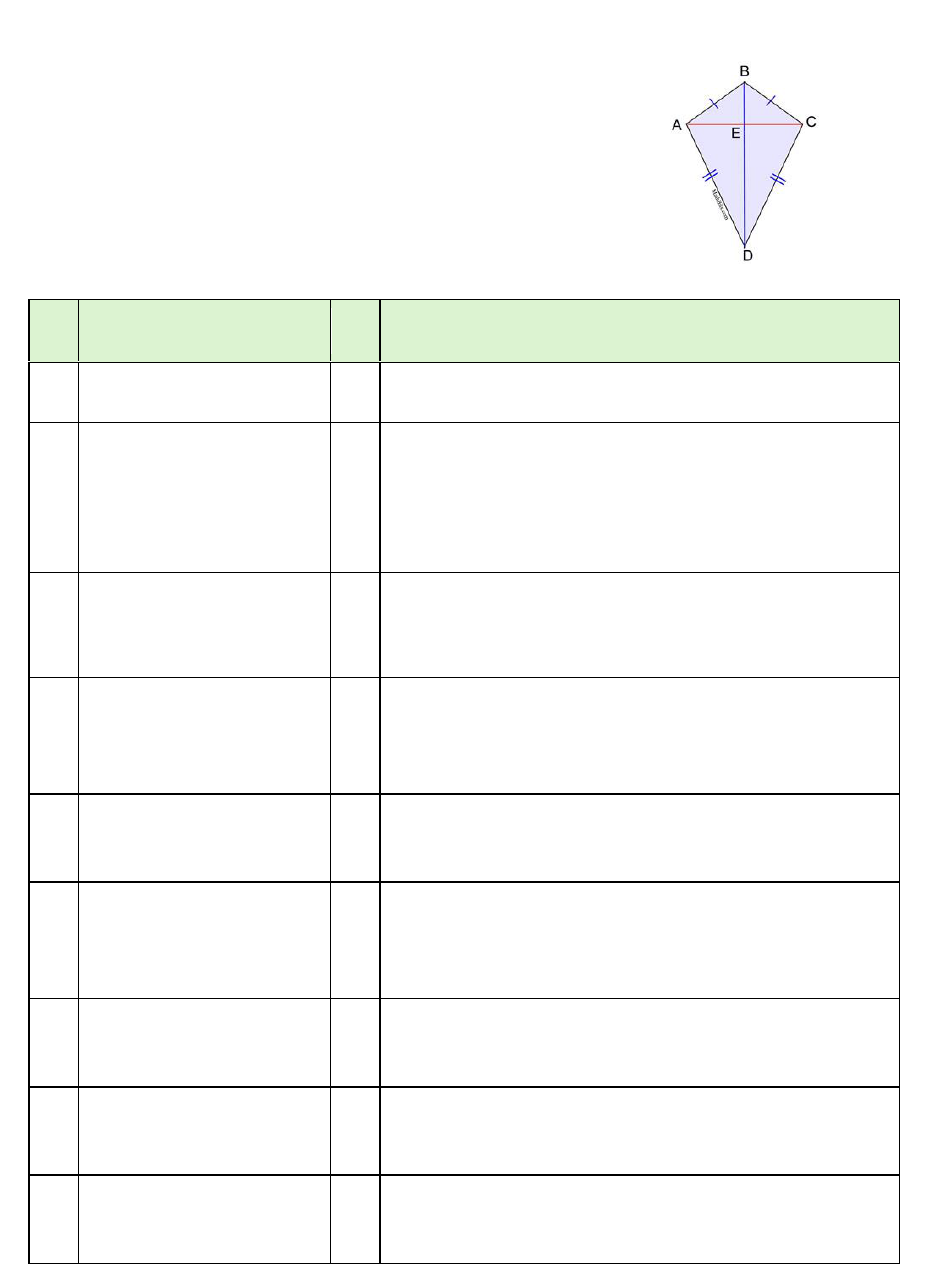
2. A kite is a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive sides that are
congruent.
In contrast to parallelograms where opposite sides are congruent, in a kite
the congruent sides are consecutive.
In the figure at the left, ABCD is a kite.
,
are consecutive sides.
are consecutive sides.
13
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Theorem
If a quadrilateral is a kite, then the diagonals are perpendicular.
If a quadrilateral is a kite, its diagonals are perpendicular.
Given: Kite ABCD
Prove:
Proof:
Statements
Reasons
1.
ABCD is a kite
1.
Given
2.
and
2.
A kite has 2 distinct pairs of congruent
consecutive sides.
3.
and
3.
Reflexive property.
4.
ΔBAD ΔBCD
4.
SSS: If 3 sides of one Δ are congruent to the
corresponding parts of another Δ, then the Δs
are congruent.
5.
ABD
CBD
5.
CPCTC: Corresponding parts of congruent Δs
are congruent.
6.
ΔBAE ΔBCE
6.
SAS: If 2 sides and the included of one Δ
are congruent to the corresponding parts of
another Δ, then the Δs are congruent.
7.
BEA
BEC.
7.
CPCTC: Corresponding parts of congruent Δs
are congruent.
8.
BEA and
BEC are
supplementary.
8.
Angles forming a linear pair are
supplementary.
9.
m
BEA + m
BEC =
180º.
9.
The sum of the measures of two
supplementary s is 180º.
14
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
10.
m
BEA = m
BEC
10.
Congruent s have equal measures.
11.
m
BEA + m
BEA =
180º.
11.
Substitution
12.
2m
BEA = 180º.
12.
Add (or combine like terms).
13.
m
BEA = 90º.
13.
Division
14.
BEA is a right angle.
14.
A right has a measure of 90º.
15.
15.
Perpendicular lines form right angles.
https://mathbitsnotebook.com/Geometry/Quadrilaterals/ThKite2Pf.html
Property
Illustration/Example
1. Diagonals of a kite are
perpendicular.
Theorem
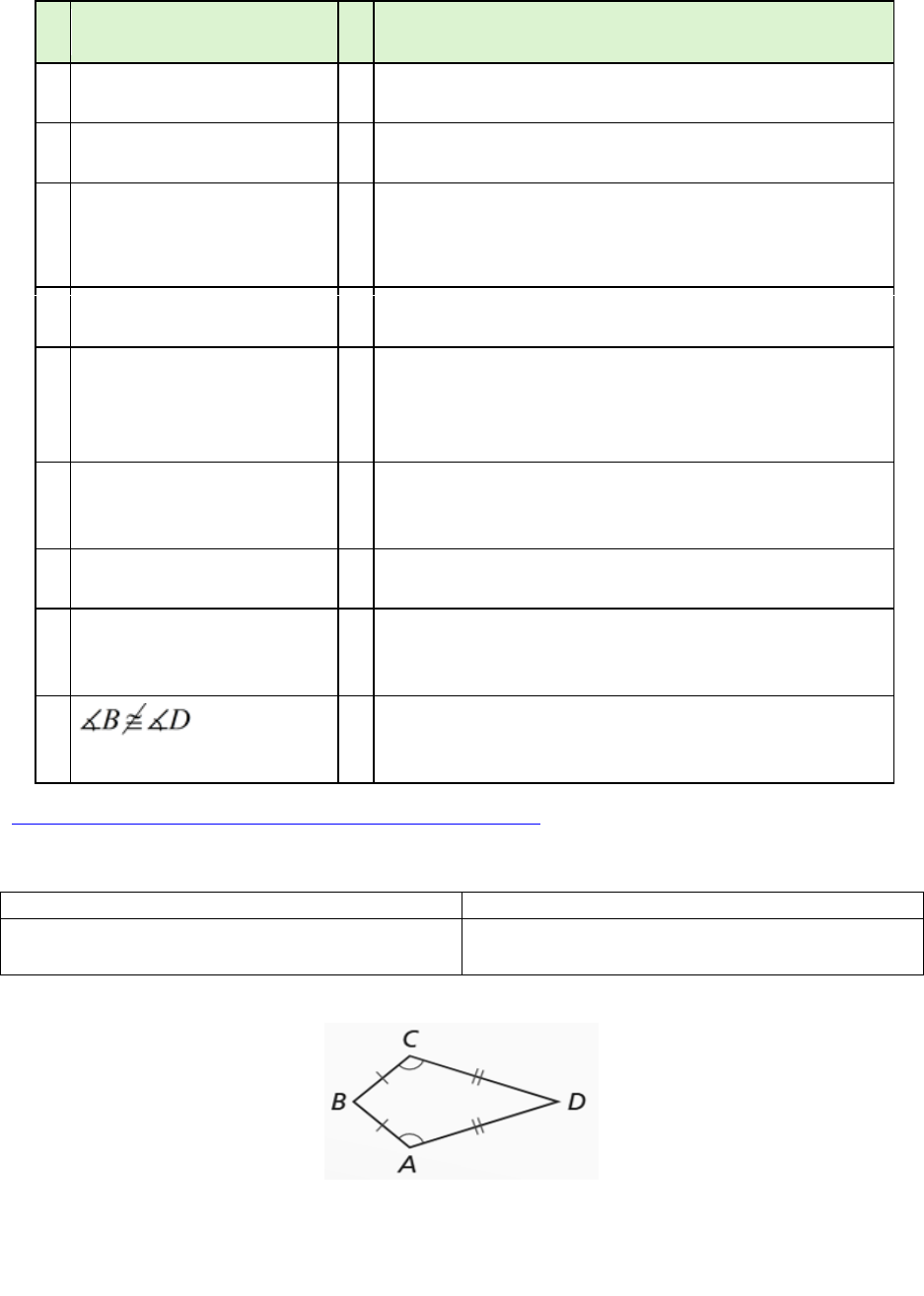
If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it has one pair of opposite congruent angles.
If a quadrilateral is a kite, it has one pair of opposite angles
congruent.
Given: Kite ABCD
Prove: C
15
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Proof:
Statements
Reasons
1.
Kite ABCD
1.
Given
2.
Draw
.
2.
Two points determine exactly one line.
3.
and
3.
A kite has 2 distinct pairs of congruent
consecutive sides.
4.
4.
Reflexive property.
5.
ΔBAD ΔBCD
5.
SSS: If 3 sides of one Δ are congruent to the
corresponding parts of another Δ, then the Δs
are congruent.
6.
A C
6.
CPCTC: Corresponding parts of congruent Δs
are congruent.
7.
Assume
B
D.
7.
Assumption leading to a contradiction.
8.
ABCD is
parallelogram
8.
If a quadrilateral has 2 pairs of opposite
congruent s, then it is a parallelogram.
9.
9.
Contradiction steps 9 and 1.
(A kite is not a parallelogram.)
https://mathbitsnotebook.com/Geometry/Quadrilaterals/ThKite1Pf.html
Property
Illustration/Example
2. Kite has exactly one pair of
opposite congruent angles.
BCD BAD
16
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Theorem
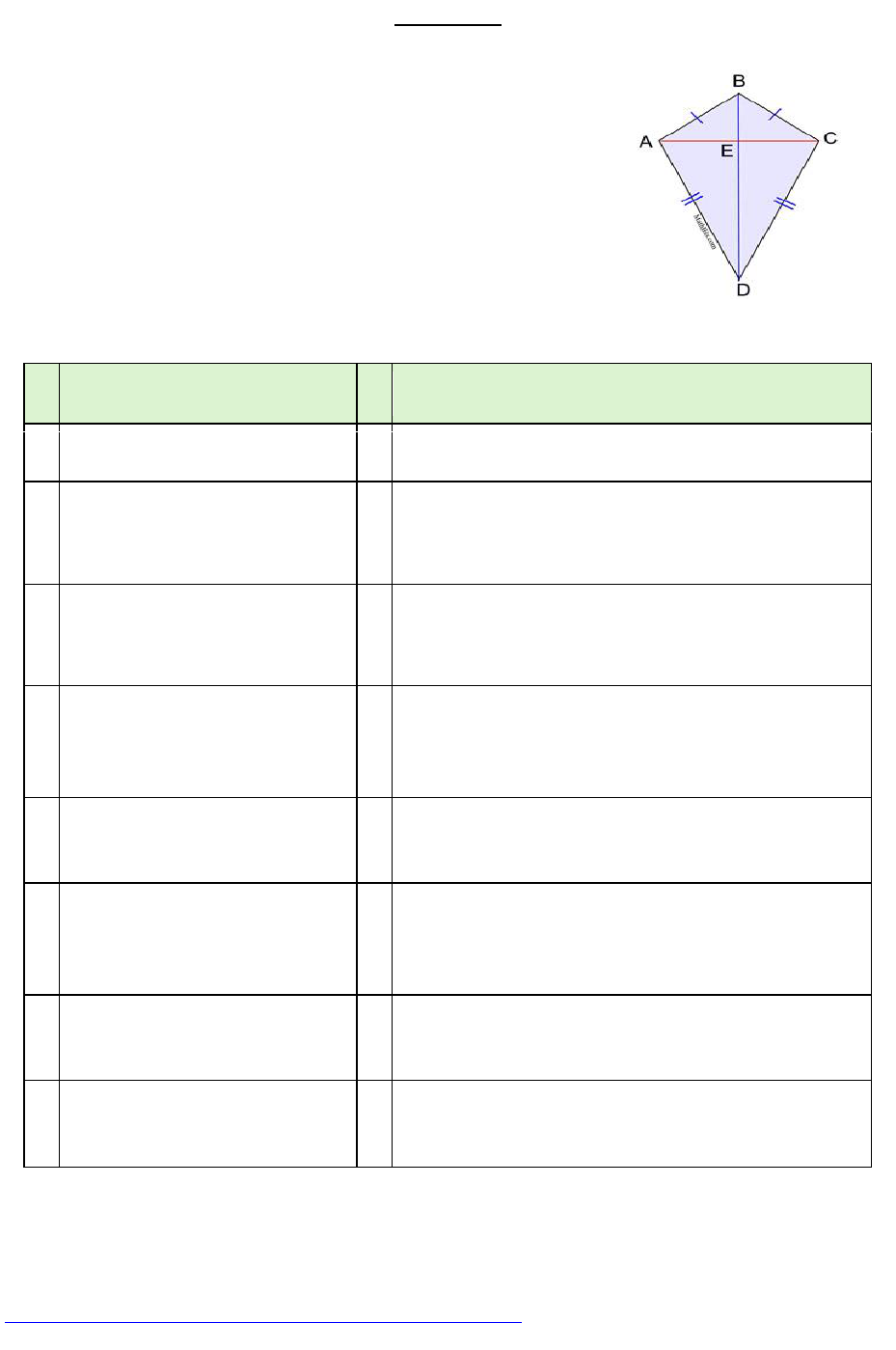
If a quadrilateral is a kite, it has one diagonal that bisects the other diagonal.
If a quadrilateral is a kite, it has one diagonal that bisects
the other diagonal.
Given: Kite ABCD
Prove: Diagonal
bisects diagonal
.
Statements
Reasons
1.
Kite ABCD
1.
Given
2.
and
2.
A kite has 2 distinct pairs of congruent
consecutive sides.
3.
and
3.
Reflexive property.
4.
ΔBAD ΔBCD
4.
SSS: If 3 sides of one Δ are congruent to the
corresponding parts of another Δ, then the
Δs are congruent.
5.
ABD
CBD
5.
CPCTC: Corresponding parts of congruent
Δs are congruent.
6.
ΔBAE ΔBCE
6.
SAS: If 2 sides and the included of one Δ
are congruent to the corresponding parts of
another Δ, then the Δs are congruent.
7.
7.
CPCTC: Corresponding parts of congruent
Δs are congruent.
8.
Diagonal
bisects
diagonal
.
8.
A segment bisector forms two congruent
segments.
There is only ONE diagonal that bisects the other. Diagonal
does not bisect diagonal
.
Since
is not congruent to
and
is not congruent to
by the definition of a kite, then
and
cannot be sides of two congruent triangle.
https://mathbitsnotebook.com/Geometry/Quadrilaterals/ThKite6Pf.html
17
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Property
Illustration/Example
3. Kite has only one diagonal
that bisects the other
diagonal.
Diagonal
bisects diagonal
.
.
4. Kite has a diagonal that
bisects each of the
noncongruent angles.
Diagonal
bisects EKI and ETI.
This means KTI KTE and IKT
EKT
What’s More
TEST YOURSELF!
Activity 3:
Using the same figure.
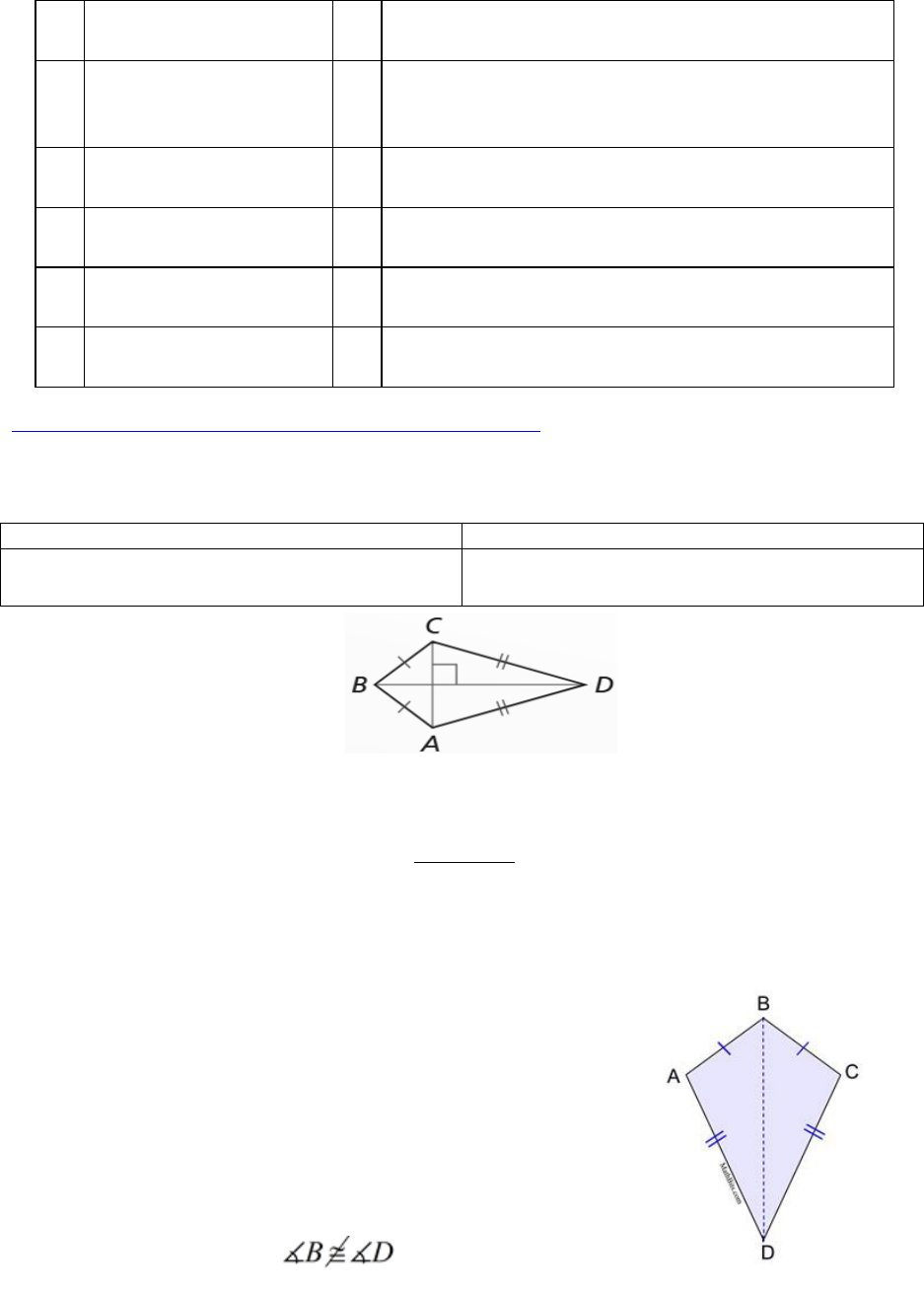
6. If |BA| = 10 cm, then |BE| = _____ and |AE| = _____.
7. If |CF| = 7.5 cm, then |DF| = _____ and |CD| = _____.
8. If |BC| = 20 cm and |AD| = 30 cm, then |EF| = _____.
9. If |BC| = 12 cm and |EF| = 18 cm, then |AD| = _____.
10. If |BC| = 23 cm, |EF| = 29 cm, and |AD| = 11x + 2, then x = ______, and
|AD| = _____.
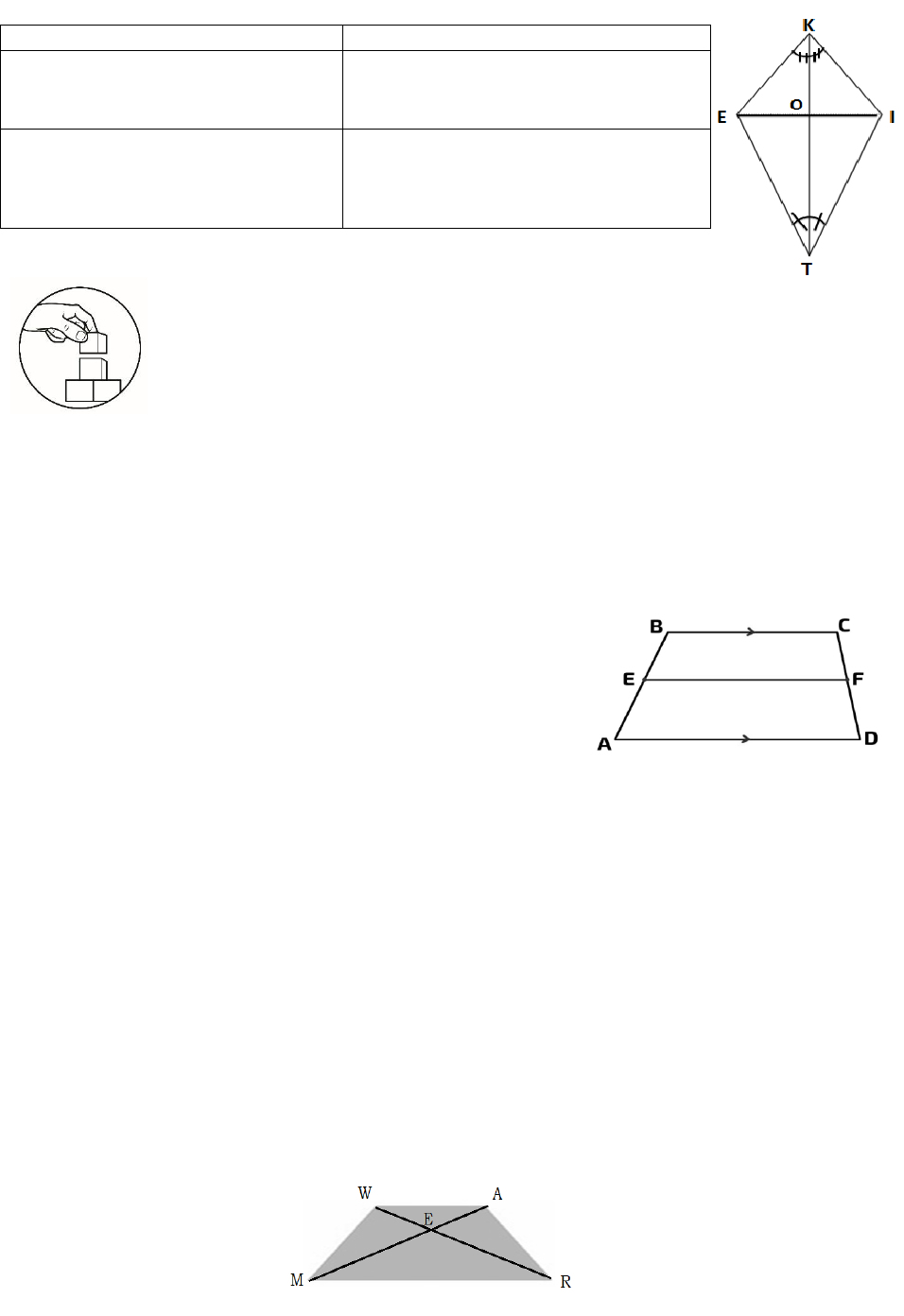
Activity 4:
A. Given is Isosceles Trapezoid WARM with diagonals WR and AM that intersect
at E.
|WM| = 17 cm, |WR| = 21 cm, |AE| = 6 cm and mWMR = 52⁰.
Given is Trapezoid ABCD at the right.
Identify the following.
1. Legs
2. Bases
3. Lower base angles
4. Upper base angles
5. Median
18
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Find the following:
1. |AR| 6. mARM
2. |AM| 7. mMWA
3. |EM| 8. mWAR
4. |WE| 9. mWMR + mWAR
5. |ER| 10. mWMR + mARM
Activity 5:
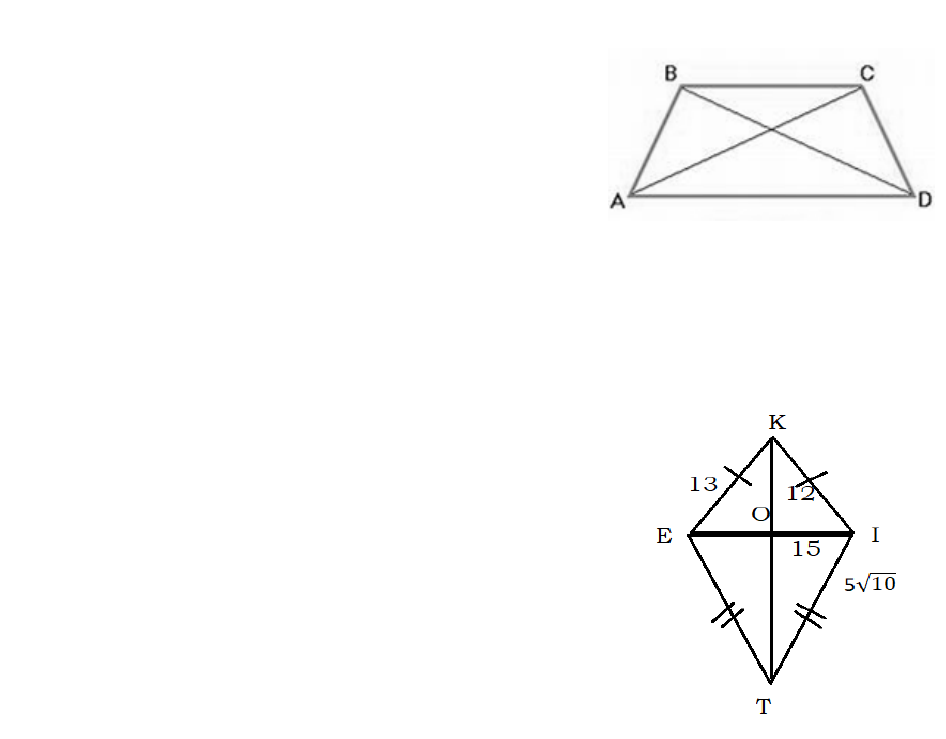
Given: KITE is a kite. Point O is the intersection of diagonals KT and EI. Find the
following:
1. mKOI
2. |KO|
3. |OI|
4. |EI|
5. |KI|
6. |ET|
7. Area of the kite
If mKET =
, mETI =
, mEKT =
, then
8. mIEK = _____.
9. mTKI = _____.
10. mEKI = _____.
11. mEIK = _____.
12. mITK = _____.
13. mKOE = _____.
14. mTOI = _____.
15. mKET + mEKI + mKIT + mITE = _____.
B. Given at the right is Isosceles Trapezoid ABCD.
|BD| = 7x and |CA| = 2x + 5 cm. Find
11. the value of x
12. |BD|
13. |CA|
19
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
What I Have Learned
What I Can Do
• A Trapezoid is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides.
The parallel sides are called bases.
The non-parallel sides are called legs.
The base angles of a trapezoid are consecutive angles with a common
side which is a base of the trapezoid.
• Length of the Median = ½ (length of upper base + length of lower base)
The median of a trapezoid is a segment joining the midpoints of the
legs.
• An isosceles trapezoid is a trapezoid whose non-parallel sides are
congruent.
Properties of an Isosceles Trapezoid
1.
The bases are parallel.
2.
The legs are congruent.
3.
The lower base angles are congruent.
4.
The upper base angles are congruent.
5.
The diagonals are congruent.
6.
The opposite angles are supplementary.
7.
Any lower base angle is supplementary to any upper base angle.
•A kite is a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive sides that are
congruent.
•In contrast to parallelograms where opposite sides are congruent, in a kite the
congruent sides are consecutive.
Properties of a Kite
1.
Diagonals are perpendicular.
2.
Has exactly one pair of opposite congruent angles.
3.
Has only one diagonal that bisects the other diagonal.
4.
Has a diagonal that bisects each of the noncongruent angles.
5.
Area of a kite = ½ (d
1
d
2
)
20
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
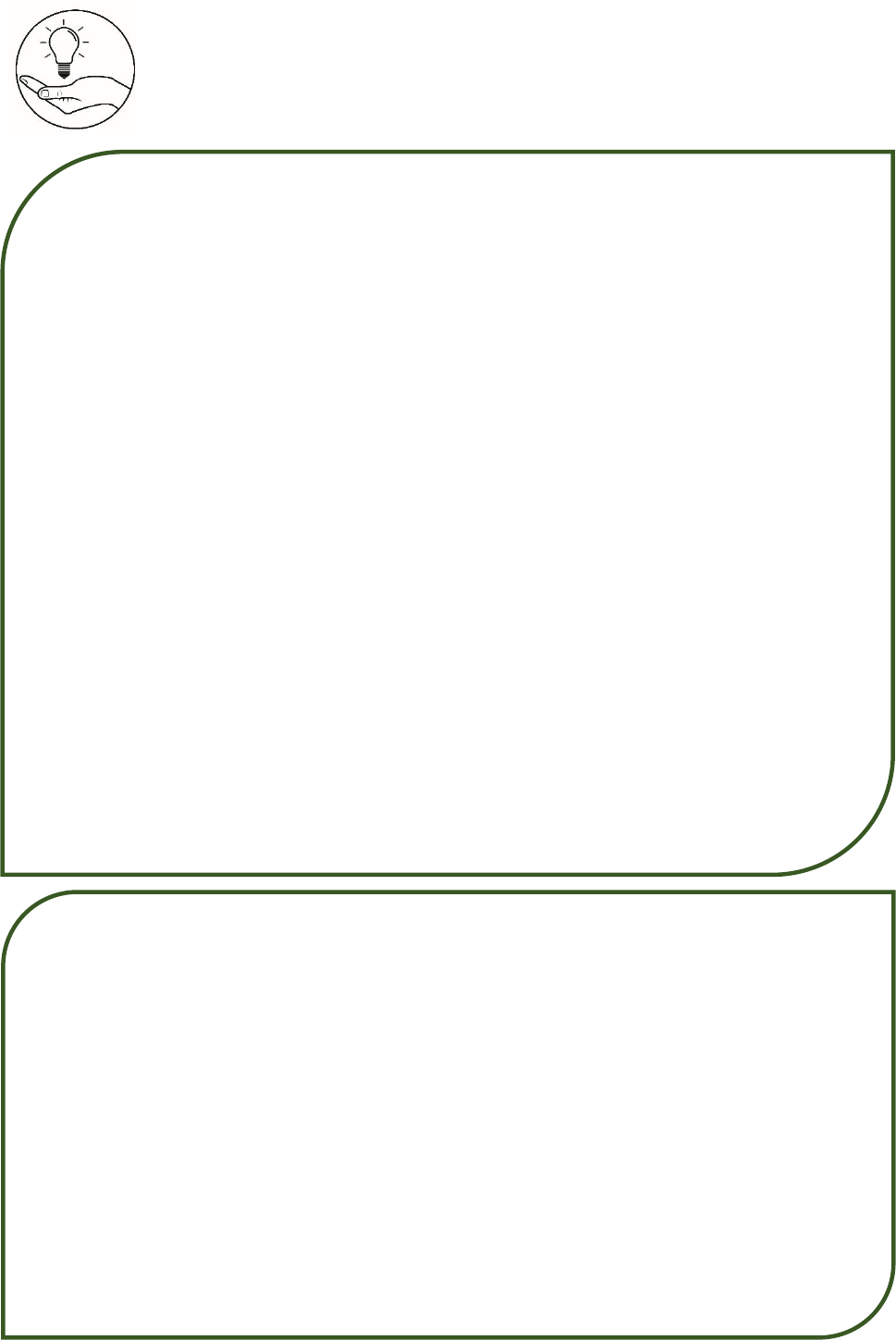
Given: LMNO is a trapezoid with
as the median. Answer each of the following
items.
Assessment
Read and answer each of the following questions accurately. Write the letter of
the correct answer on your answer sheet.
1. To find the length of the mid-segment of a trapezoid, add the lengths of the ______
and divide by two.
a.) legs b.) sides c.) bases d.) diagonals
2. The trapezoid has how many sides that are parallel to each other.
a.) 1 b.) 2 c.) 3 d.) 4
3. Which of the following statements describes a trapezoid?
a.) A quadrilateral that has two parallel sides and two non-parallel congruent
sides.
b.) A quadrilateral that has one pair of parallel sides.
c.) A quadrilateral that has no parallel sides.
d.) It is any quadrilateral.
4. Which of the following is true about isosceles trapezoids?
a.) Its diagonals are congruent.
b.) Its opposite angles are congruent.
c.) Its diagonals are perpendicular to each other.
d.) Its area is the product of the lengths of any two adjacent sides.
1. If |PQ| = 20 cm, |LM| = x + 3 cm and |ON| = x + 6 cm,
what is the value of x?
2. If |LM| = x – 2 cm, |ON| = x + 4 cm and |PQ| = 24 cm,
what is the value of x?
3. If |PQ| = 24 cm, |LM| = x + 4 cm and |ON| = x + 8 cm,
what is |LM|?
4. If |PQ| = 24 cm, |LM| = x – 3 cm and |ON| = x + 7 cm,
what is |ON|?
5. If |LM| = 12 cm, |PQ| = x + 3 cm and |ON| = x + 10
cm, what is the value of x?
6. If |LM| = 18 cm, |PQ| = x – 2 cm and |ON| = x + 3 cm,
what is the value of x?
7. If |ON| = 30 cm, |PQ| = x + 1 cm and |LM| = x – 6 cm,
what is |PQ|?
8. If |ON| = 34 cm, |PQ| = x – 1 cm and |LM| = x – 7 cm,
what is |LM|?
9. If |LM| = 2x, |PQ| = 3x and |ON| = 2(x+5), what is
|PQ|?
10. If |LM| = 2x + 2 cm, |PQ| = 3x + 3 cm and |ON| =
2(x+6), what is |LM|?

21
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
5. The median of a trapezoid measures 20 cm. One of the bases measures 12 cm.
Find the length of the other base.
a.) 20 cm b.) 24 cm c.) 28 cm d.) 32 cm
6. The legs of an isosceles trapezoid are _______.
a.) parallel c.) congruent
b.) supplementary d.) perpendicular
7. The lengths of the diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid are represented by 4x – 47
and 2x + 31. What is the value of x?
a.) 37 b.) 39 c.) 67 d.) 76
8. Which of the following is not a characteristic of an isosceles trapezoid?
a.) A lower base angle is a supplement of an upper base angle.
b.) Diagonals bisect each other.
c.) Diagonals are congruent.
d.) Legs are congruent.
9. The lower base angles of an isosceles trapezoid measure (3y – 17⁰) and (2y + 13⁰).
What is the value of y?
a.) 24⁰ b.) 30⁰ c.) 35⁰ d.) 50⁰
10. Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has parallel bases AB and CD, and diagonals intersect
at E. If |AE| = 10 cm, |BE| = 3x – 2 cm and |DE| = 4x + 1 cm, how long is
?
a.) 4 cm b.) 10 cm c.) 17 cm d.) 27 cm
11. In quadrilateral ABCD, if |AB| = |BC|, |CD| = |DA| and |AB||CD|, then the
quadrilateral is a ______.
a.) kite b.) rectangle c.) rhombus d.) trapezoid
12. Which quadrilateral has exactly one pair of opposite congruent angles?
a.) Trapezoid b.) Rectangle c.) Parallelogram d.) Kite
13. The diagonals of a kite ______.
a.) are perpendicular c.) are congruent
b.) are parallel d.) bisect each other
14. Find the area of a kite whose diagonals measure 8 cm and 20 cm.
a.) 35 sq. cm b.) 65 sq. cm c.) 70 sq. cm d.) 80 sq. cm
15. ABCD is a kite. Find the perimeter if |AB| = 6 cm and |AD| = 14 cm.
a.) 25 cm b.) 40 cm c.) 23 cm d.) 94 cm
22
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Additional Activities
Create your own real-life problem that will lead to forming trapezoid and kite.
Provide illustration of the problem and guide questions that will result to
trapezoid and kite.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
LET’S ANALYZE
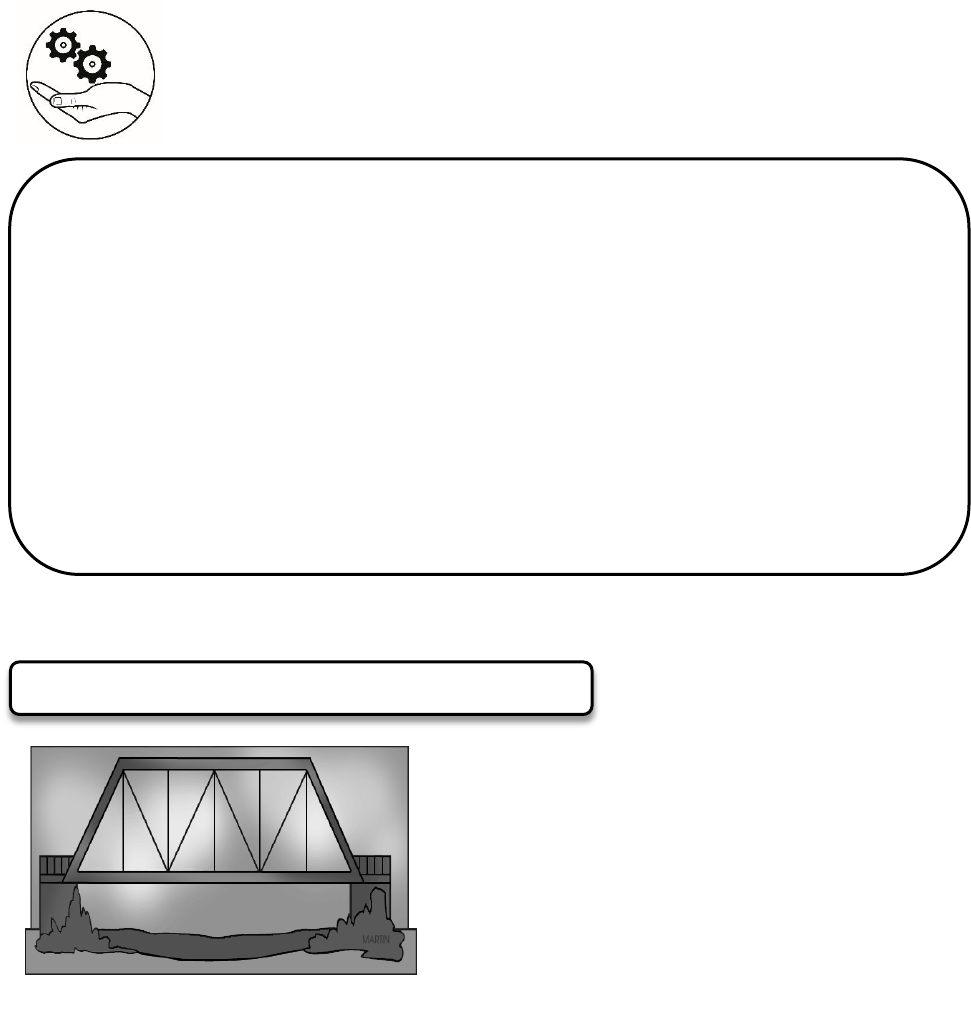
1) What is the shape of the bridge? ______
2) What is the length of the
a. top of the bridge? ______
b. bottom of the bridge? ______.
3) If the support beam is halfway between the parallel bases, what does it represent
in relation to the shape of the bridge? ______
4) What is the length of the support beam? ______
Isaac is an engineer who wants to build a
bridge to help the community in a remote
area to transport their goods. The bridge is
going to look like the figure at the left. The
top of the bridge measures 70 meters and
the bottom of the bridge measures 90
meters. He wants to build an extra support
beam halfway between the parallel bases.
PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING WORKSHEET

23
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
Answer Key
What I Know What’s More
1. C Activity 3 Activity 4 Activity 5
2. B 1. AB and CD 1. 17 1. 90
3. B 2. BC and AD 2. 21 2. 12
4. B 3. A and D 3. 15 3. 5
5. A 4. B and C 4. 6 4. 10
6. D 5. EF 5. 15 5. 13
7. C 6. 5 and 5 6. 52 6. 5
8. C 7. 7.5 and 15 7. 128 7. 135 u
2
9. B 8. 25 8. 128 8. 45
10. C 9. 24 9. 180 9. 45
10. 3 and 35 10. 104 10. 90
11. x =1 11. 45
12. BD = 7 12. 25
13. CA = 7 13. 90
14. 90
15. 360
What I Can Do Assessment Problem-Based Learning
Worksheet
1. 15.5 1. C 1. trapezoid
2. 23 2. B 2. a. 70 m b. 90 m
3. 22 3. B 3. Mid segment
4. 29 4. A 4. 80 meters
5. 16 5. C
6. 25 6. C
7. 23 7. B
8. 22 8. B
9. 15 9. B
10. 10 10. C
11. A
12. D
13. A
14. D
15. B

24
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
References
Mathematics 9 Learner’s Material, Department of Education
Nivera, G. C and Lapinid, M. R (©2013). Grade 9 Mathematics: Patterns and
Practicalities. Don Bosco Press, Inc.
Dawkin, P. (©2018). Paul's Online Math Notes. Retrieved from:
http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/Classes/Alg/SystemsTwoVrble.aspx#Sys_Tw
o_Ex1_a
http://depedk12manuals.blogspot.com
To further explore the relationships of geometric figures using
measurements, and if it possible to connect the internet, you may visit the
following links:
http://blowtheblowfish.wordpress.com/201
http://www.educationworld.com/lessonandactivites
http://www.teacherplanet.com/kites
http://youtube/Quadrilaterals:kites as a geometric shapes
http://youtube/Constructing a kite
http://youtube/proving quadrilateral kite
http://study.com/academy/practice/quiz-worksheet
http://study.com/learn/quadrilaterals-quizzes.html
http://proproofs.com/.../story.php?title=quadrilateral-quiz
http://www.mrpillarski.files.wordpress.com/2010/02/exam
http://www.mathworldhouse.com/sheets
http://www.calcworkshop.com.trapezoid/kite
E-SITES

1
CO_Q3_Mathematics 9_ Module 7
For inquiries or feedback, please write or call:
Department of Education - Bureau of Learning Resources (DepEd-BLR)
Ground Floor, Bonifacio Bldg., DepEd Complex
Meralco Avenue, Pasig City, Philippines 1600
Telefax: (632) 8634-1072; 8634-1054; 8631-4985
Email Address: blr.lrqad@deped.gov.ph * blr.lrpd@deped.gov.ph
