
Take your VITA/TCE training online at
www.irs.gov
(key word: Link & Learn Taxes). Take the Foreign Student
and Scholar and other certication tests
VITA/TCE Foreign Student and Scholar Volunteer Resource Guide
Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) / Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE)
2023 RETURNS
Publication 4011 (Rev. 10-2023) Catalog Number 34182T Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service www.irs.gov
4 0 11

CONTACTS
Common Phone Numbers/ Web Addresses/ etc.
IRS-SPEC Relationship Manager:
TaxSlayer :
Site Coordinator:
Site Leader(s):
Forms, Instructions & Publications: www.irs.gov/forms-instructions
Tax Treaties: www.irs.gov/individuals/international-taxpayers/tax-treaties
Tax Treaty Tables: www.irs.gov/individuals/international-taxpayers/tax-treaty-tables
State Government Websites: www.irs.gov/businesses/small-businesses-self-employed/state-gov-
ernment-websites
State Contact(s):
Other Contacts
EFiling Form 1040-NR through TaxSlayer -
The latest information on the preparation of Forms 1040-NR through TaxSlayer can be found by going
to the VITA/TCE Springboard at vita.taxslayerpro.com and accessing the Pro Online Knowledge-
base or Pro Desktop Knowledgebase where you will nd the applicable lesson for completing the
Form 1040-NR using either version. (Search using key word “1040-NR ”).

1
Table of Contents
Important Changes for 2023 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Foreign Student/Scholar VITA-TCE Scope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Tips for Filing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Substantial Presence Test? - Decision Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Resident or Nonresident Alien Decision Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Resident or Nonresident Alien Decision Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Form 13614-NR - Common Issues, Page 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Form 13614-NR - Common Issues, Page 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Unique Treaty Provisions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Countries with Treaty Benefits for Scholarship or Fellowship Grants (Income Code 16) . . . . . . . . 13
Countries With Treaty Benefits for Teaching and Research (Income Code 19) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Countries With Treaty Benefits for Studying and Training (Income Code 20) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Capital Gains / Losses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Dividend Income . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
State Income Tax Refunds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
How to Claim Treaty Benefits on Form 1040-NR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Schedule OI - Income Exempt from Tax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Form 1042-S Foreign Person’s U.S. Income Subject to Withholding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Filing Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Exemption Personal/Dependent Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Standard or Itemized Deduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Wage Calculation Worksheet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Tax Credits and Nonresident Aliens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Social Security and Medicare Taxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
What Form(s) to File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
When to File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Where to File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Payment Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Source Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Additional Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
General Summary of U.S. Immigration Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Job Aid-Filers without an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number or Social Security Number . . 35

2
Tax Form Changes
ITINS
• ITINs not used in the last three consecutive tax years: Any ITIN that is not
used on a federal tax return for at least three consecutive tax years will expire on
December 31 of the third consecutive tax year of non- use.
• ITINs with middle digits (the fourth and fifth positions) “70,” “71,” “72,” “73,”
“74,” “75,” “76,” “77,” “78,” “79,”“80,” “81,” “82,” “83,” “84,” “85,” “86,” “87” or “88” have
expired. In addition, ITINS with middle digits “90,” “91,” “92,” “94,” “95,” “96,” “97,”
“98,” or “99” if assigned before 2013, have expired.
Exemptions/ Dependents
• The deduction for all personal exemptions is suspended (reduced to zero), effective
for tax years 2018 through 2025.
• For 2023, the gross income limitation for a qualifying relative remains at $4,700.
Standard Deduction
The standard deduction for qualifying residents of India who may choose not to itemize
deductions on Schedule A (Form 1040-NR) has increased. The standard deduction
amounts for 2023 are:
• $27,700 - Married Filing Jointly or Qualifying Surviving Spouse (increase of $1,800)
• $13,850 - Single or Married Filing Separately (increase of $900)
Student loan interest deduction begins to phase out for taxpayers with MAGI in excess
of $75,000 ($155,000 for joint returns) and is completely phased out for taxpayers with
MAGI of $90,000 or more ($185,000 or more for joint returns).
Foreign Earned Income Exclusion
• For 2023, the maximum foreign earned income exclusion is $120,000.
Congress may enact additional legislation that will affect taxpayers after this
publication goes to print. Any changes will be reflected in Publication 4491-X, VITA /
TCE Training Supplement, available in mid-January on www.irs.gov.
Scholarship and Fellowship Grants Exclusion
Line 8r—Scholarship and fellowship grants not reported on Form W-2
Enter the amount of scholarship and fellowship grants not reported on Form W-2, reduced
by the total amount exempt by treaty. However, if you were a degree candidate at an eligible
educational organization, generally include on line 8r only the amounts you used for
expenses other than tuition, fees, and required, course-related expenses. For
example, amounts used for room, board, and travel must be reported on line 8r.
Attach any Form(s) 1042-S you receive from the educational organization to page
1 of the Form 1040-NR. Scholarship and fellowship grants are reported in box 2 of
Form 1042-S.
Important Changes for 2023

3
For more information about tax requirements for scholarships and fellowships, see Pub. 519
and chapter 1 of Pub. 970.
Under some treaties, scholarship or fellowship grant income is not exempt from
tax if the income is received in exchange for the performance of services, such
as teaching, research, or other services. Also, many tax treaties do not permit an
exemption from tax on scholarship or fellowship grant income unless the income is from
sources outside the United States. If you are a resident of a treaty country, you must
know the terms of the tax treaty between the United States and the treaty country to
claim treaty benefits on Form 1040-NR. See the instructions for item L of Schedule OI,
later, for details.
Example 1. You are a citizen of a country that does not have an income tax treaty in force
with the United States. You are a candidate for a degree at ABC University (located in the
United States). You are receiving a full scholarship from ABC University. You are not required
to perform any services, such as teaching, research, or other services, to get the scholarship,
and you have no other sources of income. The total amounts you received from ABC University
during 2022 are as follows:
Tuition and fees $25,000
Books, supplies, and equipment 1,000
Room and board 9,000
$35,000
The Form 1042-S you received from ABC University for 2022 shows $9,000 in box 2 and
$1,260 (14% of $9,000) in box 10.
Note. Box 2 shows only $9,000 because withholding agents (such as ABC University) are not
required to report section 117 amounts (tuition, fees, books, supplies, and equipment) on Form
1042-S.
You would enter $9,000 on line 8r of Schedule 1 (Form 1040) only.
Example 2. The facts are the same as in Example 1, except that you are a citizen of a country
that has an income tax treaty in force with the United States that includes a provision that
exempts scholarship income and you were a resident of that country for income tax purposes
immediately before arriving in the United States to attend ABC University. Also, assume that,
under the terms of the tax treaty, you are present in the United States only temporarily to finish
your degree, and all of your scholarship income is exempt from tax because ABC University is
a nonprofit educational organization.
When completing your tax return, do the following.
Provide all the required information in item L of Schedule OI (Form 1040-NR). Enter the $9,000
shown in box 2 of Form 1042-S into column (d) of the schedule.
Enter $9,000 from box L1(e) of Schedule OI (Form 1040-NR) on line 1k of Form 1040-NR.
Enter $1,260 on line 25g of Form 1040-NR to report the withholding shown in box 10 of Form
1042-S.
For this example, you will not enter any amount on line 8r of Schedule 1 (Form 1040)
because the entire scholarship income shown in box 2 of Form 1042-S is exempt from
tax by the treaty.
4
Foreign Student/Scholar VITA-TCE Scope
The scope of the Foreign Student and Scholar Volunteer Income Tax Assistance Program is
limited to only those areas of tax law specifically addressed in your Link and Learn training.
This occurs for many reasons:
1. It is one of our Quality Site Requirements: standards proven to provide the most consistent
quality services to the taxpayers.
2. As a volunteer you are only covered for liability while preparing returns within your IRS
certification level.
3.
Many areas of tax law, specifically treaty issues and nonresident alien issues, can be very
time consuming and would prevent the program from assisting other taxpayers with less
complex returns.
4. The VITA program should be consistent across the nation and around the globe. Services
offered in one site generally should be the same as those offered at other sites which have
volunteers of the same certification level.
If your site finds that Foreign Students and/or Scholars have similar Out of Scope issues,
you may want to refer them to other free services that can help them or advise them to seek
the services of a professional tax preparer.
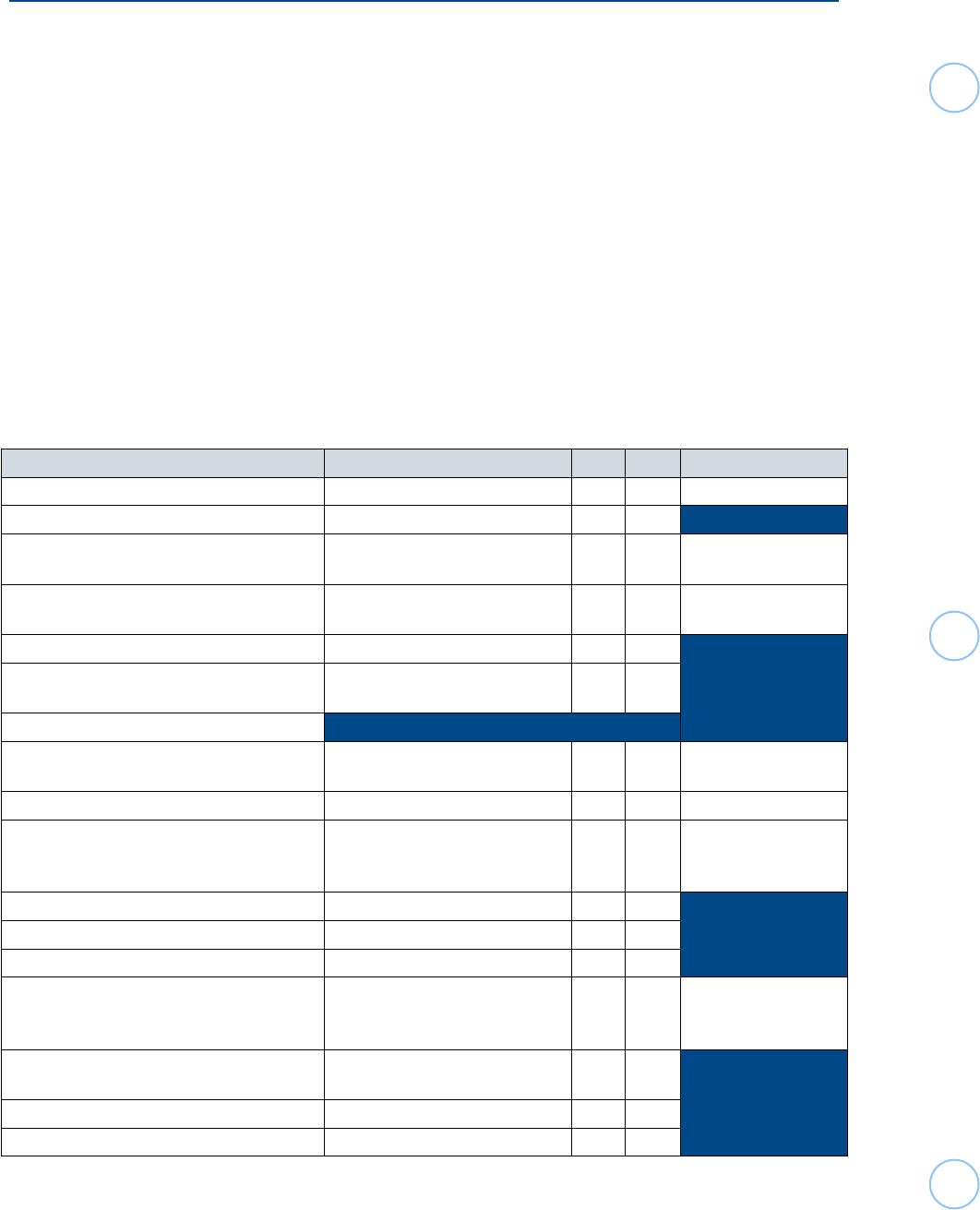
Types and Sources of Income
Income type Source is determined by IN OUT FORM 1040-NR
Dividends, with no applicable treaty benefits Where payer is incorporated X Schedule NEC
Interest - general business/investment Payer’s place of residence X
Interest - Not Effectively Connected to a U.S.
Trade or Business
Payer’s place of residence X Schedule NEC
Interest - Personal Account from a Banking
Institution
Payee’s place of residence X* Not taxable in U.S.
Gambling winnings Payer’s place of residence X
Non-Employee Compensation/ Self Employ-
ment (Form 1099-NEC, etc.)
Where services are performed X
Pension or Annuity payments attributable to:
Contributions (employer or employee, pretax)
/ Earnings of domestic (U.S.) trusts
Where the services were per-
formed/The U.S. is the source
X* Line 5a/5b
IRA distributions The U.S. is the source X* Line 4a/4b
Refunds of State & Local Income Taxes The U.S. is the source X*
Form 1040, Schedule 1,
Then Form 1040-NR,
Line 8
Rents Where property is located X
Royalties from natural resources Where property is located X
Royalties from patents, copyrights, etc. Where property is used X
Salaries, wages, and other compensation for
personal services (Listed on Forms W-2 and
1042-S codes 19 and 20)
Where services are performed X* Line 1a
Sale of inventory that was purchased Where the inventory is sold
(Where title passes)
X
Sale of personal property (except inventory) Tax home of seller X
Sale of real property Where the property is located X
* U.S. Source Only is within scope
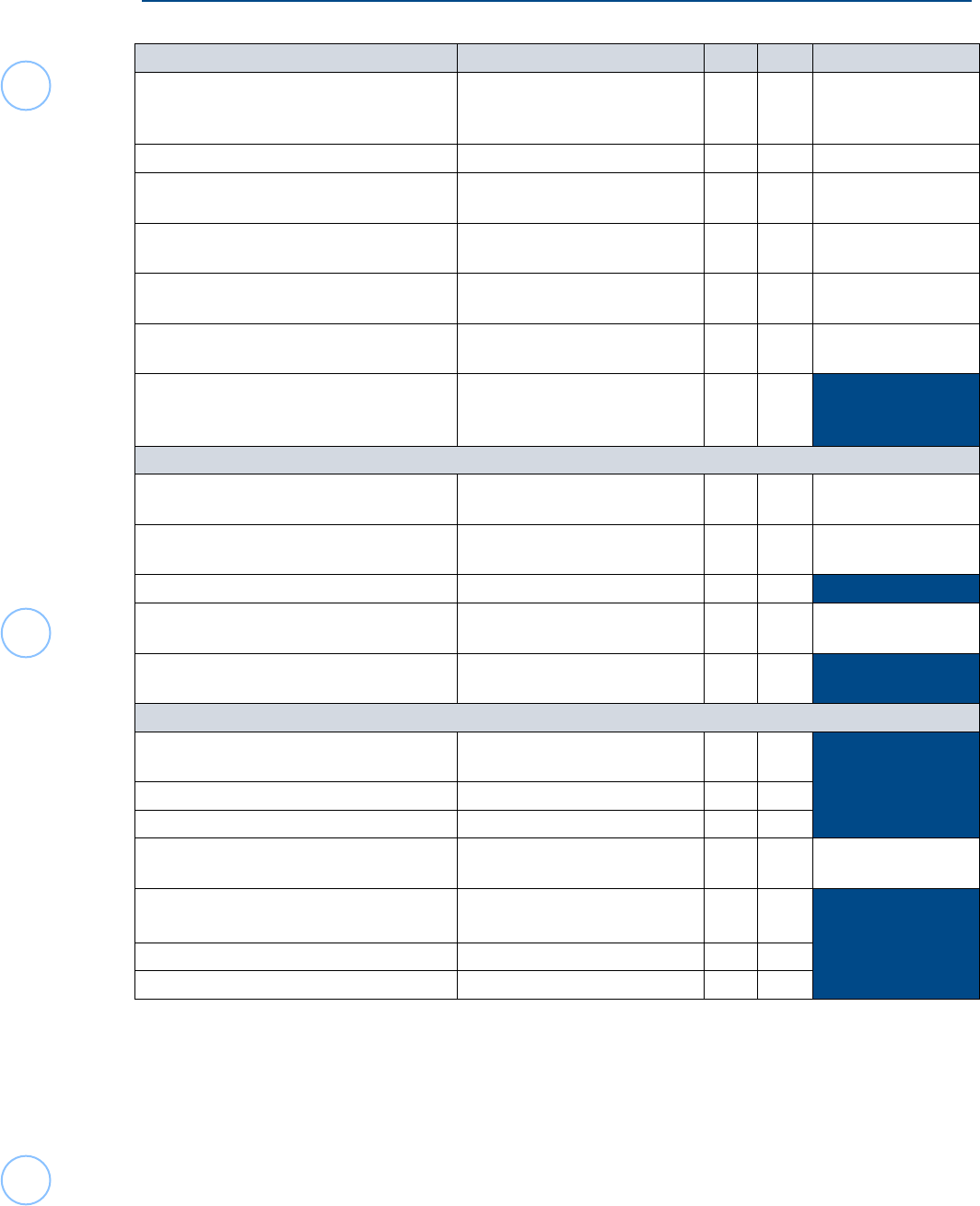
5
Foreign Student/Scholar VITA-TCE Scope
Types and Sources of Income
Income type Source is determined by IN OUT FORM 1040-NR
Taxable Scholarships and fellowships Residence of grantor X* Form 1040,
Schedule 1, Then
Form 1040-NR, Line 8
Social Security Benefits (U.S.)
Where the services were performed
X* Schedule NEC
Stock sales (Capital Gains/ Losses) sales
under $10,000
Where payer is incorporated X*
A
Schedule NEC
Unemployment Compensation Payer’s place of residence X Form 1040,
Schedule 1
Student Loan Interest Where services are performed X Form 1040,
Schedule 1
Educator Expenses, Health Savings Account,
and IRA Deductions
(Unless VITA Basic or Advanced
certified)
X
A
Form 1040,
Schedule 1
Self-Employment Tax, SEP, Penalty on Early
Withdrawal of Savings, etc. not covered in
Foreign Student Scholar Training
(Due to the complexity of these
issues for Nonresident Aliens and
possible treaty provisions, etc.)
X
Deductions:
State & Local Income Taxes U.S. Only X Form 1040-NR,
Schedule A
Gifts to U.S. Charities U.S. Only X
Form 1040-NR,
Schedule A
Casualty & Theft Losses X
Certain Misc. Deductions (Only to the extent included in the
Training Materials.)
X Form 1040-NR,
Schedule A
Medical, Mortgage Interest, Property Taxes,
etc. not listed on Form 1040-NR, Sch. A
X
Other:
Form 1095-A - Premium Tax Credits (Nonresidents are not eligible,
repayments are Out of Scope.)
X
Dual Status Residency X
Treaty Provisions claimed by a Resident Alien X
Refunds of Social Security Taxes erroneously
withheld (Form 843)
X See Form 843
Election to be treated as a Resident to file
MFJ with resident spouse
(Election Statement is Out of
Scope)
X**
Claim of “Closer Connection” or “Dual” Status X
Form W-7, ITIN Application X***
* U.S. Source Only is within scope
** A paper return can be done by a VITA/TCE site, but the election/attachment is Out of Scope.
***Only a qualied CAA site can prepare these to be sent with the return.
A
Advanced certication is also required. Refer to treaty for possible further restrictions.

6
Tips for Filing
Foreign students and scholars will have one of three statuses for tax purposes:
• Resident: U.S. residents who meet either the green card test or the substantial presence test
• Nonresident: Persons who are not U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents of the United
States
• Dual status: Persons who are both nonresidents and resident aliens in the same tax year
(Out of Scope)
If you are an exempt individual for the Substantial Presence Test you will generally file using
Form 1040-NR.
If you must apply the Substantial Presence Test and are determined to be a Resident Alien,
the normal rules and procedures for filing a Form 1040 should be followed.
If you must apply the Substantial Presence Test and are determined to be a Nonresident Alien,
you will generally file using Form 1040-NR.
1. Nonresident students, teachers, or trainees who are temporarily in the U.S. in F, J, M, or Q
immigration status must file returns if they have income that is subject to withholding, whether
tax is withheld or not.
2. Nonresident aliens claiming treaty benefits must also file a return.
Form 8843 - Who Must File
If you are an alien individual (other than a foreign government-related individual), you must file
Form 8843 yearly (for yourself and all family members in the U.S. in F-2 or J-2 immigration
status) to explain the basis of your claim that you can exclude days of presence in the United
States for purposes of the substantial presence test.
Foreign scholars or students (with or without income) excluding days of presence in the United
States because you fall into any of the following categories, must file a fully completed Form
8843.
• You were unable to leave the United States as planned because of a medical condition
or problem.
• You were temporarily in the United States as a teacher or trainee on a “J” or “Q” visa.
• You were temporarily in the United States as a student on an “F,” “J,” “M,” or “Q” visa.
7
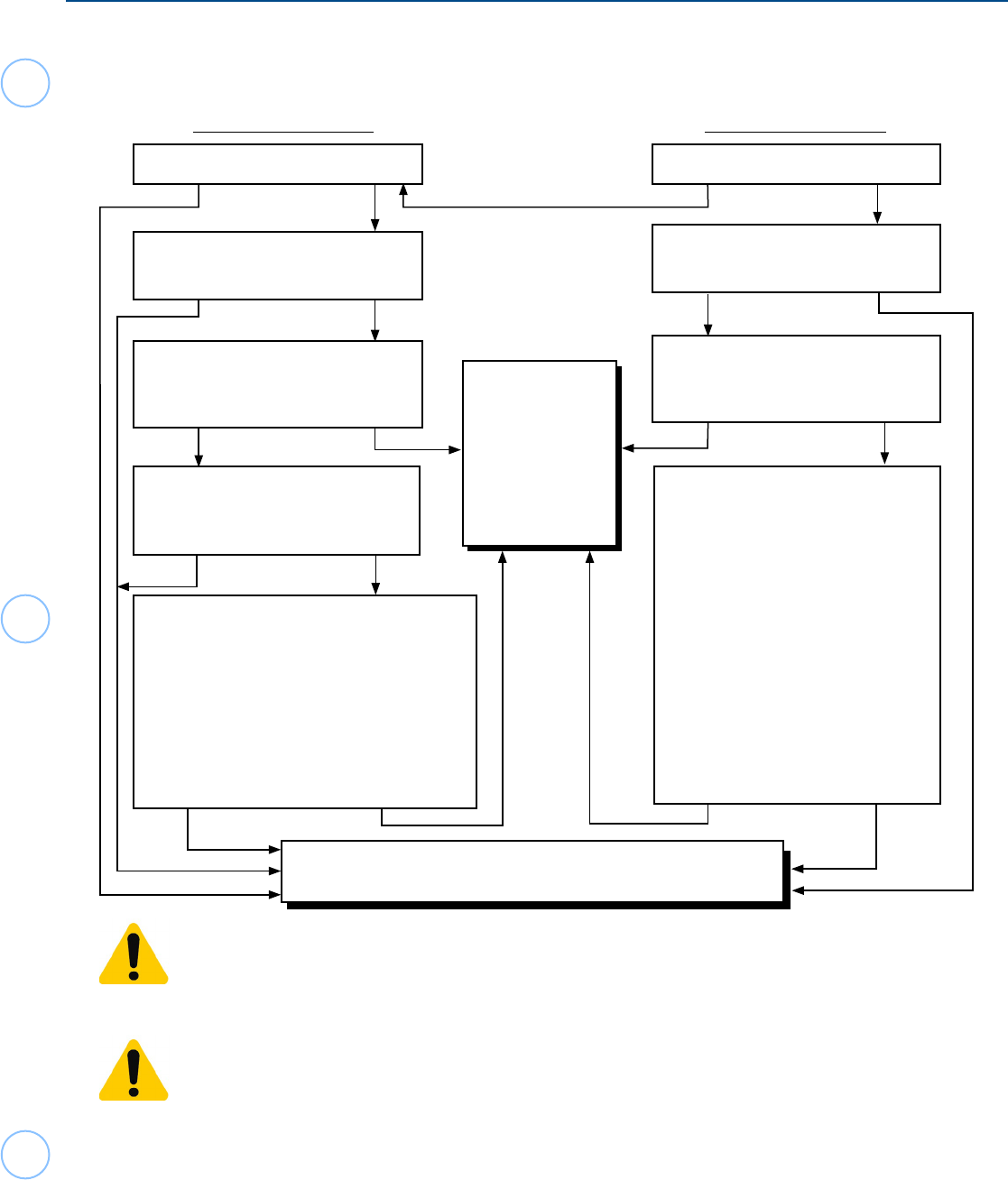
Substantial Presence Test? - Decision Tree
If you are temporarily present in the United States on an F, J, M, or Q visa, use this chart to determine if
you are an exempt individual for the Substantial Presence Test (SPT).
Do not count the following as days of presence in the United States for the substantial
presence test: Days you are an exempt individual.
If additional days of presence due to COVID-19 travel restrictions cause the taxpayer to
become a “resident” using the physical presence test rules, see possible exceptions allowed
in Revenue Procedure 2020-20.
Do you choose to claim a Closer
Connection exception to the
Substantial Presence Test?
Were you exempt as a teacher,
trainee, or student for any part of 3 (or
fewer) of the 6 preceding years, AND
Did a foreign employer pay all your
compensation during the tax year in
question, AND Were you present in
the U.S. as a teacher or trainee in
any of the preceding 6 years, AND
Did a foreign employer pay all your
compensation during each of the
preceding 6 years you were present in
the U.S. as a teacher
or trainee?
In order to claim the exception, all the
following must apply:
A. You do not intend to reside
permanently in the US
B. You must have complied with your Visa.
C. You must not have taken steps to
become a Resident Alien.
D. You must have a closer connection
to a foreign country.
No Yes
No Yes
NoYes
* You
must apply the Substantial Presence Test
using the Resident or Nonresident Alien Decision Tree
Student
F, J, M, or Q Visa
Teacher or Trainee
J Visa
Are you a student?Are you a full-time student?
Are you in substantial
compliance with your visa?
Are you in substantial
compliance with your visa?
Were you exempt as a teacher,
trainee, or student for any part of
more than 5 calendar years?
Were you exempt as a teacher,
trainee, or student for any part of 2
of the preceding 6 calendar years?
You are
an exempt
individual for the
Yes
No
Yes
No
No Yes
No Yes
No Yes
Yes No
Substantial
Presence Test
and will file
Form 1040-NR

8
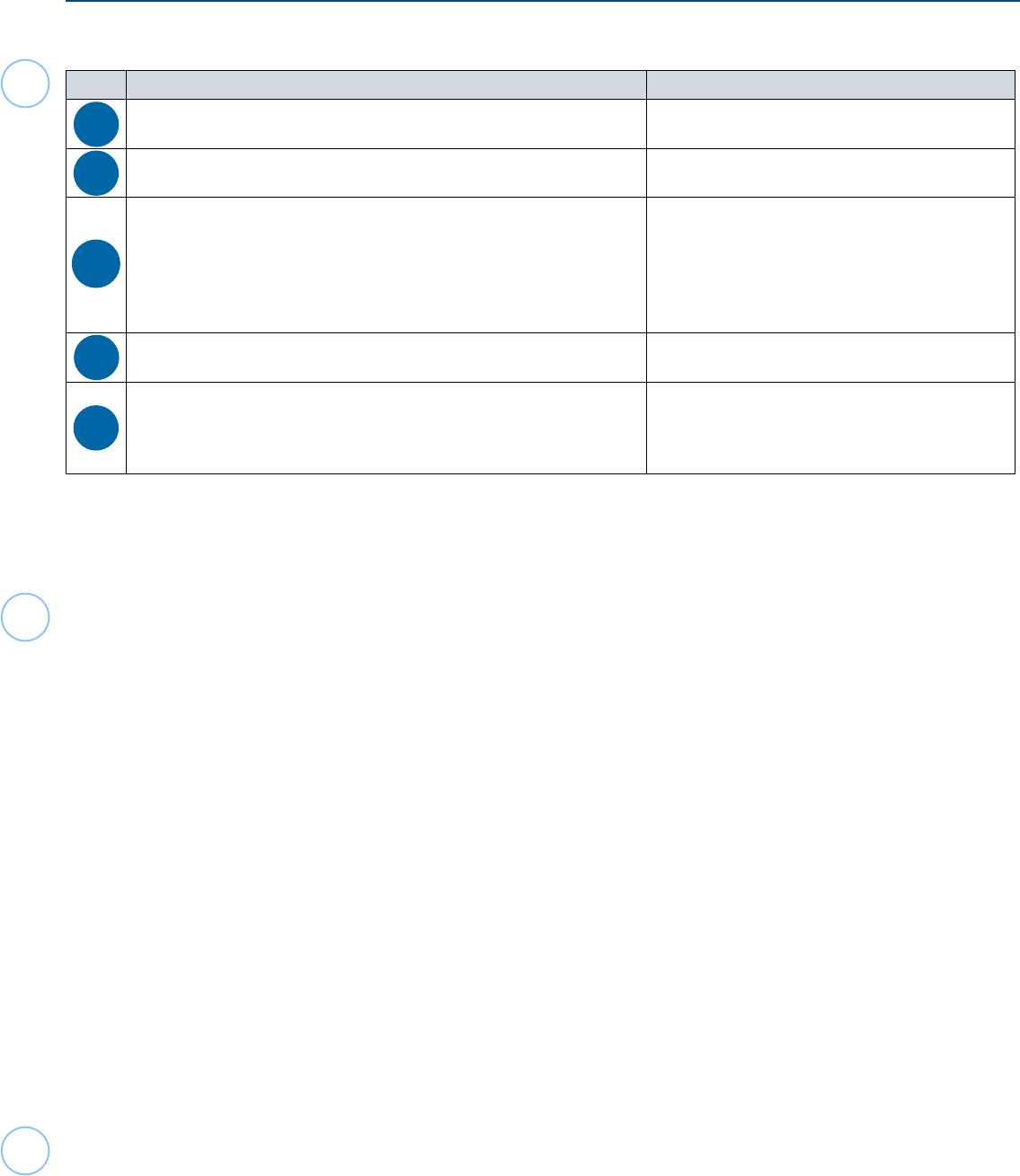
Resident or Nonresident Alien Decision Tree
Start here to determine your residency status for federal income tax purposes
Were you a lawful permanent resident of the United States (“had a green card”) at any
time during the current tax year?
1
YES NO
Were you physically present in the United States on at least 31 days during the current
tax year?
3
YES NO
Were you physically present in the United States on at least 183 days during the 3-year
period consisting of the current tax year, and the preceding 2-years, counting all days of
presence in the current tax year. 1/3 of the days of presence in the first preceding year.
and 1/6 of the days of presence in the second preceding year?
3
YES NO
4
Were you physically present in the United States on at least 183 days during the
current tax year?
3
YES NO
Can you show that for the current tax year you have a tax home in a foreign country
and have a closer connection to that country than to the United States? (*Out of
Scope, Form 8840 required)
NO YES
5
1
If this is your rst or last year of residency, you may have a dual status for the year. See Dual-Status Aliens in Pub 519. (Out of
Scope)
2
In some circumstances you many still be considered a nonresident alien and eligible for benets under an income tax treaty
between the U.S. and your country. Check the provision of the treaty carefully (Must be certied appropriately).
3
See Days of Presence in the United States in Pub 519 for days that do not count as days of presence in the U.S. (Exempt
individuals such students, scholars, and others temporarily in the U.S. under an F, J, M, or Q visa’s immigration status do not count
their days of presence in the U.S. for specied periods of time).
4
If you meet the substantial presence test for the following year, you may be able to choose treatment as a U.S. resident alien for
part of the current tax year. See Presence Test under Resident Aliens and First-Year Choice under Dual Status Aliens in Pub. 519.
(Out of Scope).
5
Nonresident students from Barbados, Hungary, and Jamaica, as well as trainees from Jamaica, may qualify for an election to be
treated as a U.S. Resident for tax purposes under their tax treaty provisions with the U.S. A formal, signed, election statement
must be attached to the Form 1040 (preparation of the statement is Out of Scope). (It continues until formally revoked).
RESIDENT Alien for U.S. Tax Purposes
1,2
NONRESIDENT Alien for U.S. Tax Purposes
9
Resident or Nonresident Alien Decision Chart
Determine residency status for federal income tax purposes.
Step Probe/Ask the taxpayer Action
1
Were you a lawful permanent resident of the United States (had a “green
card”) at any time during the current tax year?
YES – RESIDENT Alien for U.S. tax purposes
1,2
NO – Go to Step 2
2
Were you physically present in the United States on at least 31 days
during the current tax year?
3
YES – Go to Step 3
NO – NONRESIDENT Alien for U.S. tax purposes
5
3
Were you physically present in the United States on at least 183 days
during the 3-year period consisting of the current tax year and the
preceding 2 years,
counting all days of presence in the current tax year,
1/3 of the days of presence in the first preceding year, and
1/6 of the days of presence in the second preceding year?
3
YES – Go to Step 4
NO – NONRESIDENT Alien for U.S. tax purposes
4,5
4
Were you physically present in the United States on at least 183 days
during the current tax year?
3
YES – RESIDENT Alien for U.S. tax purposes
1,2
NO – Go to Step 5
5
Can you show that for the current tax year you have a tax home in a
foreign country and have a closer connection to that country than to the
United States? *(Out of Scope, Form 8840, Closer Connection Exception
Statement for Aliens required)
YES* – NONRESIDENT Alien for U.S. tax purposes
5
NO – RESIDENT Alien for U.S. tax purposes
1,2
1
If this is your rst year of residency, you may have a dual status for the year. See Dual Status Aliens in Pub 519, U.S. Tax Guide
for Aliens. (Out of Scope)
2
In some circumstances you may still be considered a nonresident alien and eligible for benets under an income tax treaty
between the U.S. and your country. Check the provision of the treaty carefully. (Out of Scope)
3
See Days of Presence in the United States in Publication 519 for days that do not count as days of presence in the U.S. (Exempt
individuals such as students, scholars, and others temporarily in the U.S. under an F, J, M, or Q visa’s immigration status do not
count their days of presence in the U.S. for specied periods of time.)
4
If you meet the substantial presence test for the following year, you may be able to choose treatment as a U.S. resident alien for
part of the current tax year. See Substantial Presence Test under Resident Aliens and First Year Choice under Dual Status Aliens
in Publication 519. (Out of Scope)
5
Nonresident students from Barbados, Hungary, and Jamaica, as well as trainees from Jamaica, may qualify for an election to be
treated as a U.S. Resident for tax purposes under their tax treaty provisions with the U.S. A formal, signed, election statement
must be attached to the Form 1040 (preparation of the statement is Out of Scope). (It continues until formally revoked.)
If after using the Resident or Nonresident Alien Decision Tree you have determined a taxpayer is a Resident
Alien for U.S. Tax Purposes, and does not meet any of the exceptions that would be outside of the scope of
the VITA program, select one of the filing statuses listed under the Basic Information Section in TaxSlayer
Pro. A Resident Alien is treated like a U.S. Citizen when determining filing status.
If after using the Resident or Nonresident Alien Decision Tree you have determined a taxpayer is a
Nonresident Alien for U.S. Tax Purposes, as the initial return screen opens or under the Basic Information
Section in TaxSlayer Pro, select Nonresident Alien, if you have certified under the Foreign Student and
Scholar Module and the taxpayer’s circumstances are within the scope of the Foreign Student and Scholar
VITA program. After selecting the Nonresident Alien filing status, you will be given three (3) choices; Single
nonresident alien, Married nonresident alien, or Qualifying Surviving Spouse.
You will only complete a tax return for a Nonresident Alien if you have certified on the Foreign Student and
Scholar Module, and at least 1 other person at your site, who is also certified on the Foreign Student and
Scholar Module, can quality review the return.
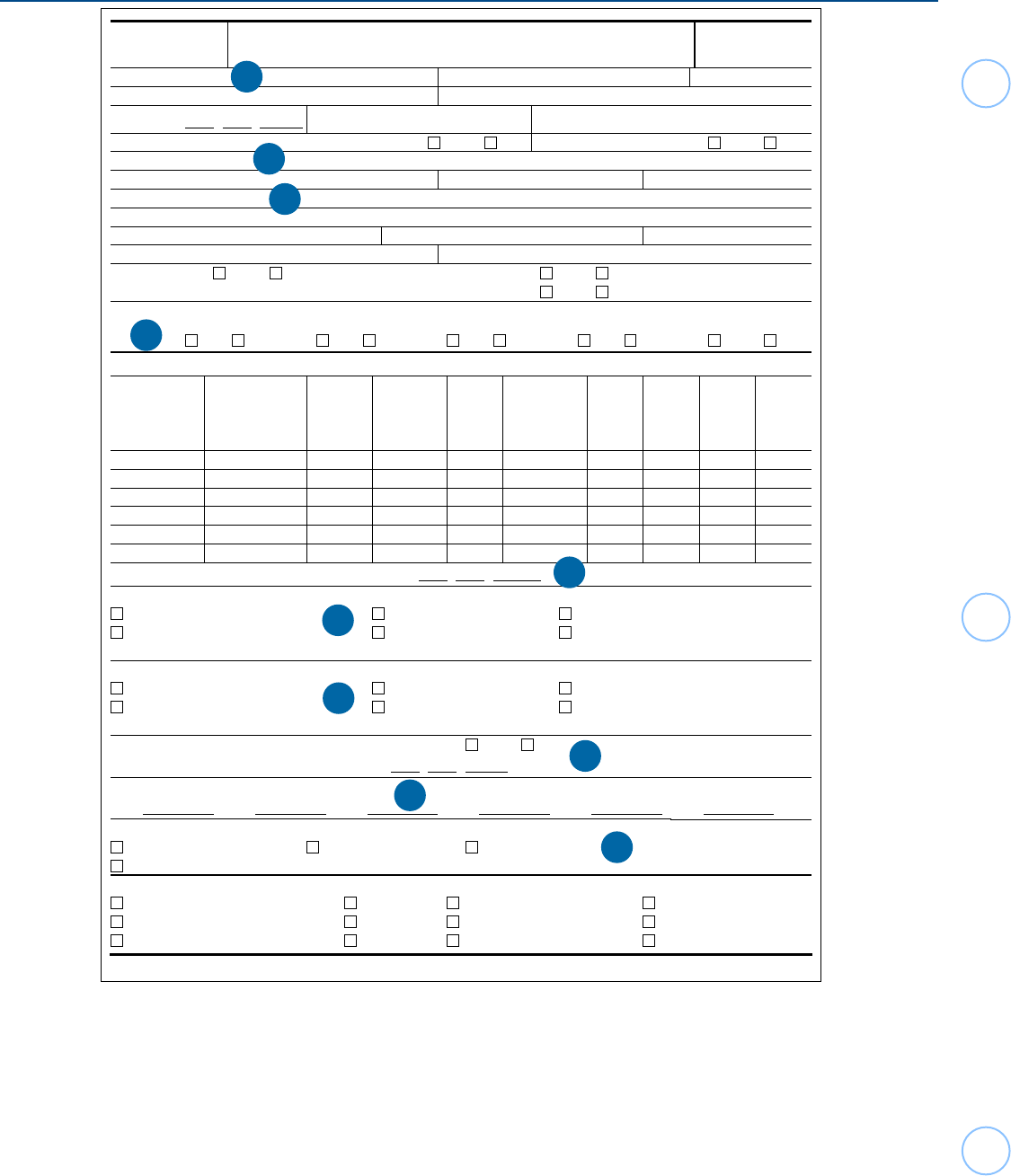
10
Form 13614-NR - Common Issues, Page 1
Catalog Number 39748B www.irs.gov
Form
13614-NR (Rev. 5-2023)
Form 13614-NR
(May 2023)
Department of the Treasury - Internal Revenue Service
Nonresident Alien Intake and Interview Sheet
OMB Number
1545-1964
Last or family name First Middle initial
Visa # Passport #
Date of birth:
(mm/dd/yyyy)
/ /
Telephone # E-mail address
Were you a U.S. citizen or resident alien the entire year? Yes No Were you ever a U.S. citizen? Yes No
U.S. local street address
City State Zip code
Foreign residence address
Address line 2
Foreign country Province/County Postal code
Country of citizenship Country that issued passport
Are you married?
Yes No If “YES”, is your spouse in the U.S.? Yes No
If "YES", is it recognized by the state where you will be filing? Yes No
Are you a U.S. National
Yes No
Resident of
Canada
Yes No
Resident of
Mexico
Yes No
Resident of
South Korea
Yes No
Resident of
India
Yes No
Dependent Information
First name
Last or
family name
Date of birth
(mm/dd/yyyy)
Relationship
to you (son,
daughter,
none, etc.)
Number of
months lived
with you in
the
U.S. in 2023
U.S. citizen,
U.S. resident alien,
U.S. national,
or a resident of
Canada, Mexico, or
South Korea
Did
person file
joint return?
Did person
provide
more than
50% of their
own
support?
Did you
provide
more than
50% of their
support?
Did the
person
have Gross
Income of
$4,700 or
more?
What is the date you FIRST entered the United States?
/ /
Entry Immigration Status - Check one
U.S. Immigrant/Permanent resident F-1 Student F-2 Spouse or child of student
H-1 Temporary employee *J-1 Exchange visitor J-2 Spouse or child of exchange visitor
Other (list)
Current Immigration Status - Check one
U.S. Immigrant/Permanent resident F-1 Student F-2 Spouse or child of student
H-1 Temporary employee *J-1 Exchange visitor J-2 Spouse or child of exchange visitor
Other (list)
Have you ever changed your visa type or U.S. immigration status? Yes No
If “Yes”, indicate the date and nature of the change.
/ /
Enter the type of U.S. visa you held during these years
2017 2018 2019 2020 2021
2022
* If Immigration status is J-1, what is the subtype? Check one
01 Student
02 Short term scholar
05 Professor 12 Research scholar
Other
(list)
What is the actual primary activity of the visit? Check one
01 Studying in a degree program
02 Studying in a non-degree program
03 Teaching
04 Lecturing
05 Observing
06 Consulting
07 Conducting research
08 Training
09 Demonstrating special skills
10 Clinical activities
11 Temporary employment
12 Here with spouse
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
1. Name should match that on Passport or Visa.
2. Taxpayer’s current address where the IRS should mail refund and/or other correspondence.
3. This is the student’s address back home, typically where the parents live. Needed if refund is to be mailed to foreign
address.
4. The answers are needed to determine if certain treaties apply. This applies to Schedule OI, Other Information.
5. Date first entered as a student/scholar.
6. Typically listed on the student/scholar’s original entry visa. Ask, as it may no longer be in the passport.
7. Current immigration status may have changed since entering the U.S. This may be needed on Schedule OI in Tax
Slayer if a treaty benefit is claimed (as well as Form 8843, Statement for Exempt Individuals With a Medical Condition).
8. Enter on Form 8843 (If you have changed your visa type of U.S. immigration status, be cautious about applying
treaty benefits properly).
9. This will indicate whether further questioning is needed to determine proper treaty benefits, as well as residency.
10. Keep in mind, a J-type visa can also include certain students, if their primary purpose is for study.

11
Form 13614-NR - Common Issues, Page 2
Catalog Number 39748B www.irs.gov
Form
13614-NR (Rev. 5-2023)
Check the years you were present in the United States as a teacher, trainee, student or as an accompanying spouse or
dependent of a person in such status for any part of the year.
2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
Have you ever been present in the U.S. PRIOR to 2017 on a teacher, trainee, student visa, or as their accompanying spouse or
dependent?
Yes No
If so, what years and visa type
How many days (including vacations, nonworkdays and partial days) were you present in the U.S. during
2021 2022 2023
List the dates you entered and left the United States during 2023
Date entered United States
mm/dd/yyyy
Date departed United States
mm/dd/yyyy
Date entered United States
mm/dd/yyyy
Date departed United States
mm/dd/yyyy
Did you file a U.S. income tax return for any year before 2023? Yes No
If “Yes”, give latest year
/ /
Form number filed
During 2023, did you apply to be a green card holder (lawful permanent resident) of the United States? Yes No
Do you have an application pending to change your status to lawful permanent resident? Yes No
1. Are you claiming the benefits of a U.S. income tax treaty with a foreign country?
Yes No
If “Yes”, enter the appropriate information in the columns below
(a) Country (b) Tax treaty article
(c) Number of months
claimed in prior tax years
(d) Amount of exempt
income in current tax year
2. Were you subject to tax in a foreign country on any of the income shown in 1(d) above? Yes No
Information about academic institution you attended in 2023
Name Telephone number
Address
Name of your academic/specialized program director
Address
Telephone number
During 2023 did you receive
Scholarships or fellowship grants Yes No
Wages, salaries or tips Yes No
Interest Yes No
Distributions from IRA, pension or annuity
Yes No
State or local tax refunds Yes No
Unemployment compensation Yes No
Dividend income or capital gains or losses Yes No
Any other income (gambling, lottery, prizes, awards, self-employment, rents, royalties, virtual currency, etc.) Yes No
Did you have
Casualty losses in a declared disaster
area
Yes No
Student loan interest paid Yes No
State or local income taxes Yes No
U.S. Charitable contributions Yes No
Child/Dependent care expenses Yes No
IRA contributions Yes No
Did you or any dependent have health insurance coverage through HealthCare.gov (The Marketplace)?
NoYesIf yes, was any Advanced Premium Tax Credit received? (Provide Form 1095-A)
Yes No
Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice
The Privacy Act of 1974 requires that when we ask for information we tell you our legal right to ask for the information, why we are asking for it, and how it will be used. We
must also tell you what could happen if we do not receive it, and whether your response is voluntary, required to obtain a benefit, or mandatory.
Our legal right to ask for information is 5 U.S.C. 301. We are asking for this information to assist us in contacting you relative to your interest and/or participation in the IRS
volunteer income tax preparation and outreach programs. The information you provide may be furnished to others who coordinate activities and staffing at volunteer return
preparation sites or outreach activities. The information may also be used to establish effective controls, send correspondence and recognize volunteers. Your response is
voluntary. However, if you do not provide the requested information, the IRS may not be able to use your assistance in these programs.
The Paperwork Reduction Act requires that the IRS display an OMB control number on all public information requests. The OMB Control Number for this study is 1545-2075.
Also, if you have any comments regarding the time estimates associated with this study or suggestion on making this process simpler, please write to the Internal Revenue
Service, Tax Products Coordinating Committee, SE:W:CAR:MP:T:T:SP, 1111 Constitution Ave. NW, Washington, DC 20224.
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
11. For use in determining exempt days status. (Students may exempt only 5 years TOTAL)
12. Partial days count as full days, unless a Canadian or Mexican commuter with +75% workdays commuting.
(Entered on Form 8843 in TaxSlayer)
13. Most tax years end 12/31/XXXX. List Form 1040, 1040-NR etc., as appropriate.
14. Most treaty articles are listed under income codes 16, 19 or 20 later in this publication. Enter these on Schedule OI.
15. If more than one academic institution was attended during the tax year, use the most recent prior to 01/01/2023.
This information will be used on Form 8843 in TaxSlayer.
16. The school or other payer may provide information for scholarships, grants, wages and salaries electronically and/
or paper form with various formats. Inquire about all sources of income and deductions in this section.
17. Advise taxpayer of record requirements for charitable contributions.
18. Caution: While most student/scholars have insurance provided through their sponsoring school, organization, etc.,
some may have applied for coverage through the Marketplace and erroneously received a Premium Tax Credit that
needs to be repaid.

12
Unique Treaty Provisions
United States-India Income Tax Treaty, Article 21(2)
An Indian student or apprentice may take a standard deduction equal to the amount allowable on Form
1040 and may be able to claim the personal exemptions for a nonworking spouse and U.S. born-children.
However, benefits will be limited to certain credits, as the allowable exemption deduction is currently -0- until
2025.
Treaty benefits for a scholar from India are very different from those for a student. The scholar benefit for
income code 19 is lost retroactively if the visit exceeds 2 years.
Generally, the standard deduction for Single taxpayers and Married Filing Separately taxpayers in 2023 is
$13,850.
Nonresident aliens can’t file a joint return. Even though a student from India may be able to take an
exemption for a nonworking spouse, this is not considered a joint return. Thus, the standard deduction for
married filing separately must be used. In determining their tax liability, they must use the tax tables or tax
rate schedules for married filing separately.
United States-People’s Republic of China Treaty, Articles 19, 20(c)
Almost all U.S. tax treaties are limited to a specific number of years and may not be available for U.S.
residents for tax purposes. An exception is the United States-People’s Republic of China Treaty. Its
provisions are not limited by year restrictions.
Also: This treaty is not applicable to Chinese citizens who are residents of Hong Kong, Macao, or Taiwan.
The United States-People’s Republic of China Treaty provides that a scholar is exempt from tax on earned
income for 3 years. After 2 years, a scholar will become a resident alien for tax purposes but is still entitled
to 1 more year of tax benefits under the treaty. The treaty also provides that students have an exemption of
up to $5,000 per year for income earned while they are studying or training. In most cases, the student will
become a resident for federal tax purposes in their sixth calendar year. Students from the People’s Republic
of China can continue to claim the treaty benefits on their resident alien tax return (if they still meet the
definition of a student).
United States-Canada Income Tax Treaty, Article 15
The students and scholars are permitted to use Article 15 of the tax treaty, which applies to dependent
personal services.
Students and scholars making use of the treaty benefits for dependent and independent personal service
income (Income Codes 17 and 18) remain Out of Scope for the VITA/TCE Foreign Student and Scholar
Program and must be referred to a professional tax preparer.
The tax treaty with Canada is different from most other tax treaties because it (1) exempts all earned income
if the nonresident earned not more than $10,000 in the tax year, but (2) taxes all income if the nonresident
earned more than $10,000. This treaty benefit is lost if the nonresident becomes a resident for tax purposes.

13
* Commonwealth of Independent States (Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan
and Uzbekistan.) Generally, limited to $10,000 p.a. of scholarship/fellowship income to provide ordinary living expenses.
Country
Maximum
Years in U.S.
Maximum
Dollar Amounts
Treaty
Article
Bangladesh 2 No Limit 21(2)
China, People’s Republic of No Limit No Limit 20(b)
Commonwealth of Independent States* 5 Limited VI(1)
Cyprus 5 No Limit 21(1)
Czech Republic 5 No Limit 21(1)
Egypt 5 No Limit 23(1)
Estonia 5 No Limit 20(1)
France 5 No Limit 21(1)
Germany No Limit No Limit 20(3)
Iceland 5 No Limit 19(1)
Indonesia 5 No Limit 19(1)
Israel 5 No Limit 24(1)
Kazakhstan 5 No Limit 19
Korea, South 5 No Limit 21(1)
Latvia 5 No Limit 20(1)
Lithuania 5 No Limit 20(1)
Morocco 5 No Limit 18
Netherlands 3 No Limit 22(2)
Norway 5 No Limit 16(1)
Philippines 5 No Limit 22(1)
Poland 5 No Limit 18(1)
Portugal 5 No Limit 23(1)
Romania 5 No Limit 20(1)
Russia 5 No Limit 18
Slovak Republic 5 No Limit 21(1)
Slovenia 5 No Limit 20(1)
Spain 5 No Limit 22(1)
Thailand 5 No Limit 22(1)
Trinidad and Tobago 5 No Limit 19(1)
Tunisia 5 No Limit 20
Ukraine 5 No Limit 20
Venezuela 5 No Limit 21(1)
Countries with Treaty Benefits for Scholarship or Fellowship Grants
(Income Code 16)
If a nonresident alien receives a grant that is not from U.S. sources, it is not subject to U.S. tax.
Scholarship or fellowship grants that cover tuition and fees (and books and supplies if required of all
students) are not subject to U.S. tax. (Financial aid that is dependent on the performance of services,
such
as a teaching assistant, is treated as wages and subject to the code income 18, 19, or 20 provisions.)
Scholarship or fellowship grants that cover room, board and other personal expenses are subject
to U.S. tax unless a treaty benefit (as summarized below) exists.

14
Country
Maximum
Years in U.S.
Maximum
Dollar Amounts
Treaty
Article
Bangladesh 2 No Limit* 21(1)
Belgium 2 No Limit 19(2)
Bulgaria 2 No Limit 19(2)
China, People’s Republic of 3 No Limit 19
Commonwealth of Independent States** 2 No Limit VI(1)
Czech Republic 2 No Limit 21(5)
Egypt 2 No Limit 22
France 2 No Limit 20
Germany 2 No Limit 20(1)
Greece 3 No Limit XII
Hungary 2 No Limit 17
India 2L No Limit 22
Indonesia 2 No Limit 20
Israel 2 No Limit 23
Italy 2 No Limit 20
Jamaica 2 No Limit 22
Japan 2 No Limit 20
Korea, South 2 No Limit 20
Luxembourg 2L No Limit 21(2)
Netherlands 2L No Limit 21(1)
Norway 2 No Limit 15
Pakistan 2L No Limit XII
Philippines 2 No Limit 21
Poland 2 No Limit 17
Portugal 2 No Limit 22
Romania 2 No Limit 19
Slovak Republic 2 No Limit 21(5)
Slovenia 2 No Limit 20(3)
Thailand 2L No Limit 23
Trinidad and Tobago 2 No Limit 18
Turkey 2 No Limit 20(2)
United Kingdom 2L No Limit 20A
Venezuela 2 No Limit 21(3)
Countries with Treaty Benefits for Teaching and Research
(Income Code 19)
The following is a quick-reference summary of treaty benefits. For more information about the
application of these treaty benefits, see Publication 901.
* 2-year limit applies to business or technical apprentices.
** Commonwealth of Independent States (Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan
and Uzbekistan.)
L
Treaty contains provisions that retroactively eliminates benefits if the allowable period in the U.S. or income amounts are
exceeded as defined in the treaty.

15
Country
Maximum
Years in U.S.
Maximum
Dollar Amounts
Treaty
Article
Bangladesh No Limit* $8,000 21(2)
Belgium No Limit 9,000 19(1)(b)
Bulgaria No Limit 9,000 19(1)(b)
China, People’s Republic of No Limit 5,000 20(c)
Cyprus 5 2,000 21(1)
Czech Republic 5 5,000 21(1)
Egypt 5 3,000 23(1)
Estonia 5 5,000 20(1)
France 5 5,000 21(1)
Germany 4L 9,000 20(4)
Iceland 5 9,000 19(1)
Indonesia 5 2,000 19(1)
Israel 5 3,000 24(1)
Korea, South 5 2,000 21(1)
Latvia 5 5,000 20(1)
Lithuania 5 5,000 20(1)
Luxembourg 2L No Limit 21(2)
Malta No Limit 9,000 20(2)
Morocco 5 2,000 18
Netherlands No Limit 2,000 22(1)
Norway 5 2,000 16(1)
Pakistan No Limit 5,000 XIII(1)
Philippines 5 3,000 22(1)
Poland 5 2,000 18(1)
Portugal 5 5,000 23(1)
Romania 5 2,000 20(1)
Slovak Republic 5 5,000 21(1)
Slovenia 5 5,000 20(1)
Spain 5 5,000 22(1)
Thailand 5 3,000 22(1)
Trinidad and Tobago 5 2,000 19(1)
Tunisia 5 4,000 20
Venezuela 5 5,000 21(1)
Countries With Treaty Benefits for Studying and Training (Income Code 20)
The following is a quick-reference summary of treaty benefits. For more information about the
application of these treaty benefits, see Publication 901.
* 2-year limit applies to business or technical apprentices.
L
Treaty contains provisions that retroactively eliminates benefits if the allowable period in the U.S. or income amounts are
exceeded as defined in the treaty.
Tax Treaty provisions allowed federally may not be honored by some states. Contact your
state to see if treaty provisions are honored on the state return.

16
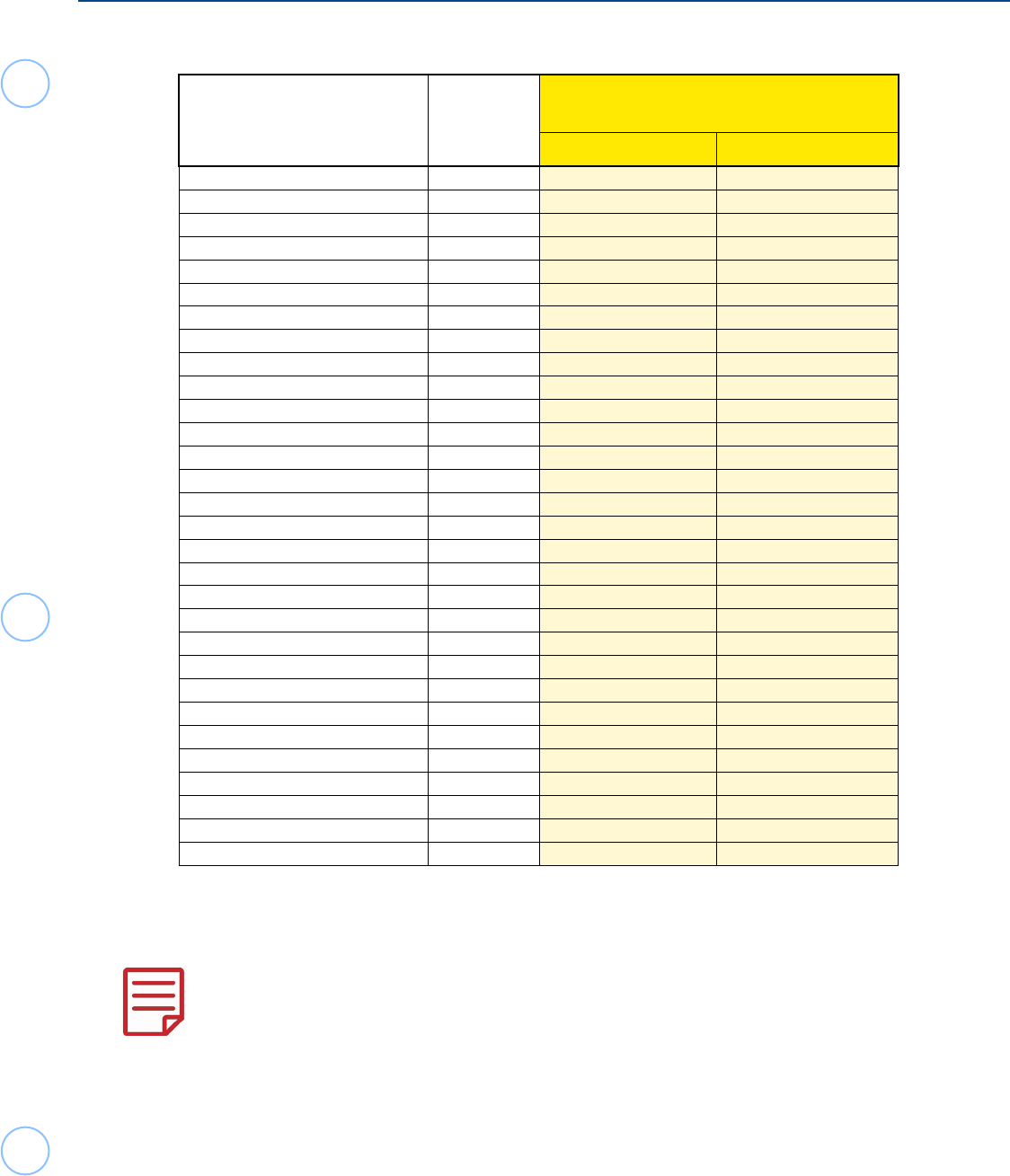
Capital Gains / Losses
The only capital gains/losses within the scope of the Foreign Student & Scholar VITA program are
related to the sale of U.S. stocks, generally considered NOT effectively connected with the taxpayer’s U.S.
trade or business. All other sales of property remain Out of Scope.
If a nonresident alien is physically present in the U.S. for less than 183 days during the tax year, none of
the capital gains from these sales are taxable. The days counted for excludable gains consider all days of
presence, regardless of exempt days based on visa status under IRC §7701(b).
If the nonresident is present in the U.S. for 183 days or more, generally the rate of tax on the gain is 30%.
This income is reported on Form 1040-NR, U.S. Non Resident Alien Income Tax Return, Schedule NEC,
Tax on Income Not Effectively Connected With a U.S. Trade or Business, NOT on Schedule D, Capital
Gains and Losses, nor on the income section of Form 1040-NR. Capital losses of nonresident aliens may
only offset other capital gains. (Capital losses of nonresident aliens cannot be used against other income,
nor can they be carried forward to another tax year.)
Some tax treaties provide an exclusion from tax on various capital gains relating to stock sales. The
following countries have a tax treaty with the U.S. If the table below indicates a potential 0% tax, review all
paragraphs of the treaty article fully to ensure all conditions are met (reported on Schedule NEC). (Some
treaties limit the percentage of stock ownership held or types of assets held by the corporation, etc.)
Tax Treaties Taxation Rate - Capital Gains (from Sales of U.S. Stocks)
Treaty Country
Country
Code
Capital Gains from
U.S. Corporate Stock sales
Rate
Treaty Article Citation
Australia
AS 30% none
Austria AU 0 13(6)
Bangladesh BG 0 13(4)
Barbados BB 0 13(6)
Belgium BE 30% 13(3)
Bulgaria BU 0 13(8)
Canada CA 0 XIII(4)
China, People’s Republic of CH 30% 12
Comm. of Independent States* - 0 IIII(1)(b)
Cyprus CY 0 16(1)
Czech Republic EZ 0 13(6)
Denmark DA 0 13(6)
Egypt EG 30% 14(1)(d)
Estonia EN 0 13(6)
Finland FI 0 13(6)
France FR 0 13(6)
Germany GM 0 13(5)
Greece GR 30% none
Hungry HU 0 12(3)
Iceland IC 0 13(6)
India IN 30% 13
Indonesia ID 30% 14(2)(b)
Ireland EI 0 13(5)
Israel IS 30% 15(1)(d)
Italy IT 0 13(4)
Jamaica JM 0 13(6)
Japan JA 0 13(7)
Kazakhstan KZ 0 13(6)
Korea, South KS 0 13(6)
17
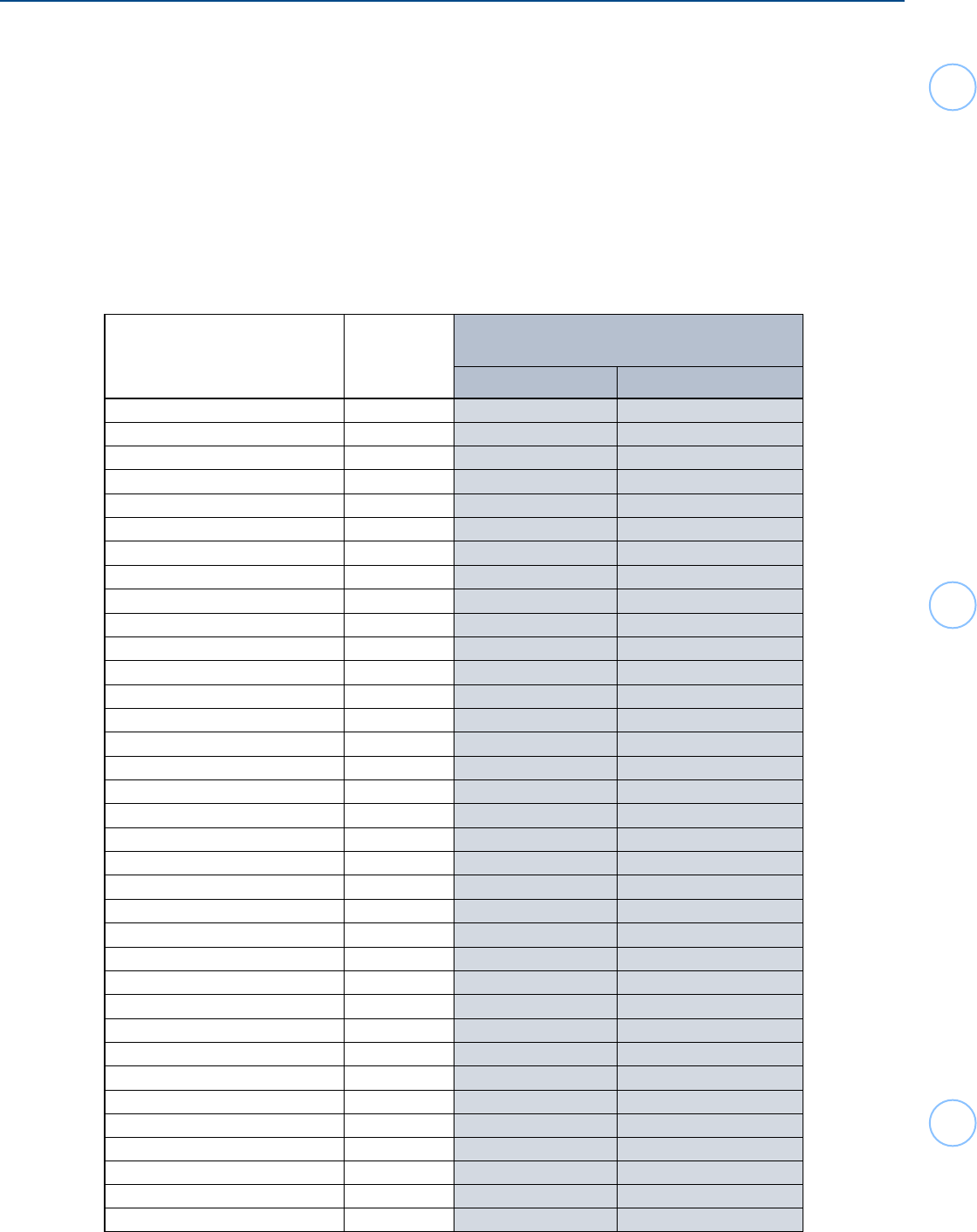
Treaty Country
Country
Code
Capital Gains from
U.S. Corporate Stock sales
Rate Treaty Article Citation
Latvia LG 0 13(6)
Lithuania LH 0 13(6)
Luxembourg MT 0 14(5)
Malta MX 0 13(6)
Mexico BE 0 13(7)
Morocco MO 0 13(2)(c)(ii)
Netherlands NL 0 14(7)
New Zealand NZ 0 13(7)
Norway NO 30% 12(1)(c)(ii)
Pakistan PK 30% none
Philippines RP 0 14(2)
Poland PL 0 14(7)
Portugal PO 0 14(6)
Romania RO 30% 13(1)(b)
Russia RS 0 21(4)
Slovak Republic LO 0 13(6)
Slovenia SI 0 13(5)
South Africa SF 0 13(5)
Spain SP 0 13(7)
Sri Lanka CE 0 13(7)
Sweden SW 0 13(6)
Switzerland SZ 0 13(5)
Thailand TH 30% 13
Trinidad & Tobago TD 30% –
Tunisia TS 0 13(5)
Turkey TU 0 13(5)
Ukraine UP 0 13(4)
United Kingdom UK 30% 13
Venezuela VE 0 13(5)
Other Countries – 30% –
* Those countries to which the U.S.-U.S.S.R. income tax treaty still applies: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus,
Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan,Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan.
Nonresident aliens residing in the U.S. for less than 183 days in the tax year, generally
are exempt from tax on Capital gains from U.S. stock sales.
Tax Treaties Taxation Rate - Capital Gains (from Sales of U.S. Stocks)
Capital Gains / Losses
18
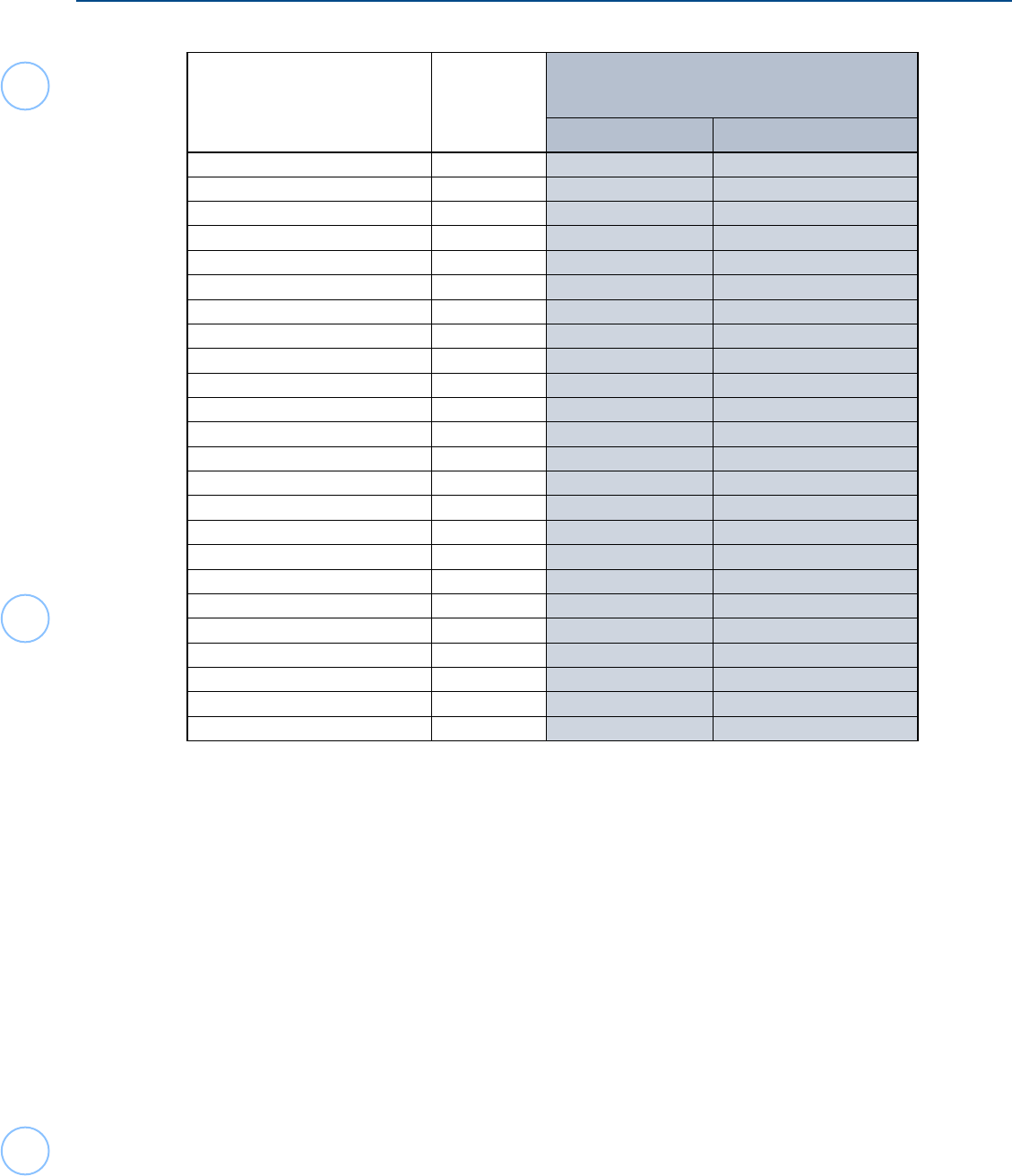
Dividend Income
Generally, dividend income from investments in U.S. corporate stock is considered FDAP (Fixed,
Determinable, Annual or Periodic) income, NOT effectively connected to the taxpayer’s U.S. trade or
business and is therefore taxable at a 30% rate on Form 1040-NR, Schedule NEC, NOT on the income
section on the front of Form 1040-NR.
The U.S. has income tax treaties with a number of foreign countries. These treaties can often reduce or
eliminate U.S. income tax on various types of income, such as dividends, if certain conditions are met.
Carefully read the tax treaty article and the conditions allowing for reduced rates. Many of these reduced
rates only apply to regulated investment companies (RICs) or a real estate investment trusts (REITs).
Below is a list of the treaty countries and the treaty article and protocol potentially allowing reduced rates.
Dividend income for the nonresident aliens is subject to 30% income tax rate, unless a lower rate is allowed by
treaty. These lower treaty rates are Out of Scope for the VITA/TCE Foreign Student and Scholar program.
Tax Treaties / Taxation Rate - Dividends (paid by U.S. Corporations)
Treaty Country
Country
Code
Dividends paid by
U.S. Corporations (general)
Rate Treaty Article Citation
Australia AS 15mm 10(2)/P6
Austria AU 15w 10(2)
Bangladesh BG 15mm 10(2)
Barbados BB 15w, rr 10(2)/1PIII(1); 2PII(6)
Belgium BE 15dd, mm 10(2)
Bulgaria BU 10dd, mm 10(2)
Canada CA 15mm X(2)/5P5(1)
China, People’s Republic of CH 10 9(2)
Comm. of Independent States* – 30 None
Cyprus CY 15 12(2)
Czech Republic EZ 15w 10(2)
Denmark DA 15dd, mm 10(2)/PII
Egypt EG 15 11(2)
Estonia EN 15w 10(2)
Finland FI 15dd, mm 10(2)/PIII
France FR 15mm 10(2)/2P2
Germany GM 15dd, mm 10(2)/PIV
Greece GR 30 none
Hungry HU 15 9(2)
Iceland IC 15dd, mm 10(2)
India IN 25w 10(2)
Indonesia ID 15 11(2)/P1
Ireland EI 15mm 10(2)
Israel IS 25w 12(2)
Italy IT 15mm 10(2)
Jamaica JM 15 10(2)/P2
Japan JA 10dd, mm 10(2)
Kazakhstan KZ 15ff 10(2)
Korea, South KS 15 12(2)
Latvia LG 15w 10(2)
Lithuania LH 15w 10(2)
Luxembourg LU 15w 10(2)
Malta MT 15dd, mm 10(2)
Mexico MX 10dd. mm 10(2)/2PII
Morocco MO 15 10(2)
19
Treaty Country Country
Code
Dividends paid by
U.S. Corporations (general)
Rate Treaty Article Citation
Netherlands NL 15dd, mm 10(2)/P3(a)
New Zealand NZ 15mm 10(2)/PVI
Norway NO 15 8(2)/PVI(1)
Pakistan PK 30 VII(2)/VI(1)
Philippines RP 25 11(2)
Poland PL 15 11(2)
Portugal PO 15w 10(2), (3)
Romania RO 10 10(2)
Russia RS 10ff 10(2)
Slovak Republic LO 15w 10(2)
Slovenia SI 15mm 10(2)
South Africa SF 15w 10(2)
Spain SP 15w 10(2)
Sri Lanka CE 15gg 10(2)
Sweden SW 15dd, mm 10(2)/PIV
Switzerland SZ 15w, dd 10(2)
Thailand TH 15w 10(2)
Trinidad & Tobago TD 30 12(1)
Tunisia TS 20w 10(2)
Turkey TU 20w 10(2)
Ukraine UP 15ff 10(2)
United Kingdom UK 15mm 10(2)
Venezuela VE 15mm 10(2)
Other Countries – 30 None
* Those countries to which the U.S.-U.S.S.R. income tax treaty still applies: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belaru
Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan,Turkmenistan, & Uzbekistan.
w
The rate applies to dividends paid by a regulated investment company (RIC) or a real estate investment trust
(REIT). However, that rate applies to dividends paid by a REIT only if the beneficial owner of the dividends is
an individual holding less than a 10% interest (25% in the case of Portugal, Spain, Thailand, and Tunisia) in
the REIT.
dd
Amounts paid to certain pension funds that are not derived from the carrying on of a business, directly or indi-
rectly, by the fund are exempt. This includes dividends paid by a REIT only if the conditions in footnote mm
are met. For Sweden, to be entitled to the exemption, the pension fund must not sell or make a contract to
sell the holding from which the dividend is derived within 2 months of the date the pension fund acquired the
holding. The United States has competent authority arrangements (MAP) with some treaty jurisdictions (e.g.
Netherlands and Switzerland) that describe which pension funds are eligible for the exemption. See the Com
petent Authority Arrangements page on irs.gov.
ff
The rate applies to dividends paid by a regulated investment company (RIC). Dividends paid by a real estate
investment trust (REIT) are subject to a 30% rate.
gg
In Sri Lanka, the rate applies to dividends paid by a real estate investment trust (REIT) only if the beneficial
owner of the dividends is (a)an individual holding less than a 10% interest in the REIT, (b) a person holding not
more than 5% of any class of the REIT’s stock and the dividends are paid on stock that is publicly traded, or
(c) a person holding not more than a 10% interest in the REIT and the REIT is diversified.
mm
The rate applies to dividends paid by a regulated investment company (RIC) or real estate investment trust
(REIT). However, that rate applies to dividends paid by a REIT only if the beneficial owner of the dividends is
(a) an individual (or pension fund, in some cases) holding not more than a 10% interest in the REIT, (b) a
person holding not more than 5% of any class of the REIT’s stock and the dividends are paid on stock that is
publicly traded, or (c) a person holding not more than a 10% interest in the REIT and the REIT is diversified.
Dividend Income
Tax Treaties / Taxation Rate - Dividends (paid by U.S. Corporations)

20
pp
The rate applies to dividends paid by a regulated investment company (RIC) or real estate investment trust
(REIT). However, that rate applies to dividends paid by a REIT only if the beneficial owner of the dividends is
(a) an individual holding not more than a 25% interest in the REIT, (b) a person holding not more than 5% of
any class of the REIT’s stock and the dividends are paid on stock that is publicly traded, or (c) a person hold-
ing not more than a 10% interest in the REIT and the REIT is diversified, or (d) a Dutch belegginginstelling.
rr
The rate applies to dividends paid by a regulated investment company (RIC) or a real estate investment trust
(REIT). However, that rate applies to dividends paid by a REIT only if the beneficial owner of the dividends is
an individual holding less than a 10% interest (25% in the case of Portugal, Spain, Thailand, and Tunisia) in
the REIT.
State Income Tax Refunds
If the taxpayer itemized in 2022 that included a deduction for state income tax, and received a state refund in
2023, that refund may be included as income on the 2023 tax return.
Students may have received taxable refunds of state and/or local taxes. Remember that nonresident
students, except from India, must itemize their deductions. This can include state and local income taxes
paid. Any refund of state and local taxes may need to be included on the return in the year received.
Students from India are allowed a standard deduction. If the standard deduction was used on the previous
year’s tax return, do not include the amount of any state or local tax refund in taxable income.
21
How to Claim Treaty Benefits on Form 1040-NR
Nonresident aliens may claim treaty benefits on Form 1040-NR.
If a taxpayer is a resident alien eligible to claim treaty benefits on Form 1040, the return is Out of
Scope for the VITA/TCE Foreign Student and Scholar program.
The following shows how to claim treaty benefits listed on Form 1042-S, Foreign Person’s U.S. Source
Income Subject to Withholding.
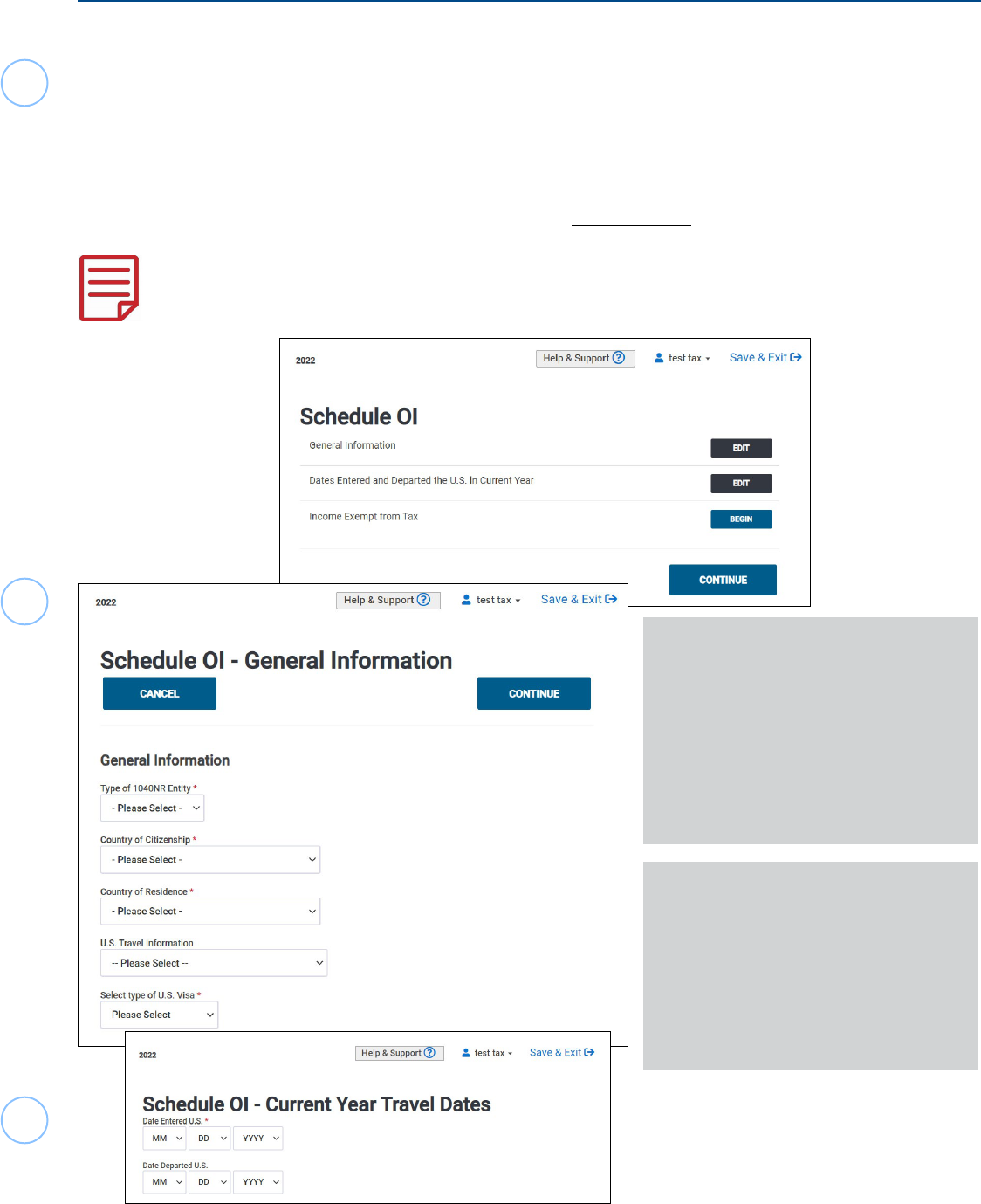
First, enter the necessary information based on the F13614-NR, Nonresident Alien Intake and Interview
Sheet entries, and your interview with the taxpayer for the three sections of Schedule OI in TaxSlayer.
This section shows how to enter the Form 1042-S, however, a taxpayer who received a Form W-2,
Wage and Tax Statement, or other income statement may also be eligible to exclude income under
their treaty. This section of the software would be used for these taxpayers, as well.
The Schedule OI menu will
automatically open after entering
Dependents / Qualifying Person
selections in the software.
Complete all sections on the Schedule
OI Menu; General Information, Dates
Entered and Departed the U.S. in
Current Year, and Income Exempt from
Tax.
For a taxpayer who does not receive
Form 1042-S and is entitled to claim
treaty benets rst complete the
Schedule OI-General Information with
the allowable treaty benet amount
listed under Wages Exempt by a treaty.
Next, move to Schedule OI- Income
Exempt from Tax and re-enter the
amount of exempt income.
22
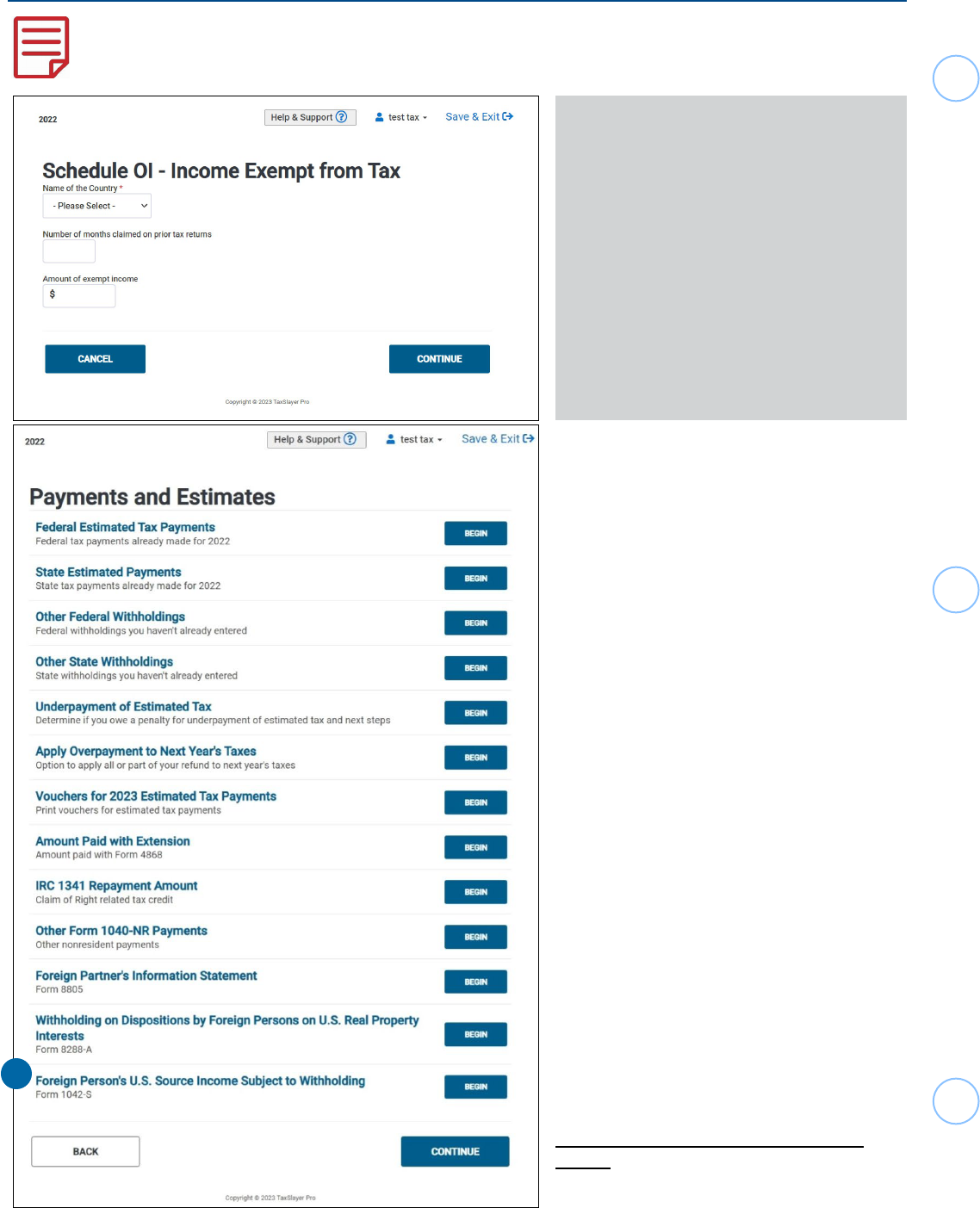
Schedule OI - Income Exempt from Tax
List the country from which the taxpayer
is claiming treaty benets. Once entered,
another box will appear with a drop-down
menu asking which treaty article is being
applied.
If this treaty benet has been used on
PRIOR returns, list the total number of
months the article has been used in
PRIOR years.
List the amount of income THIS year that is
to be exempt from taxation due to the treaty
article. (Remember, if the amount received
is less than the amount excludable by treaty,
list the amount received.)
Federal Section>Payments and Estimates>Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject
to Withholding
1.
Next, you will enter the information
from each box on the Form 1042-S into
the software.
Only enter information for completed
boxes. Each entry has the same
corresponding title as listed on the form
.
1
23
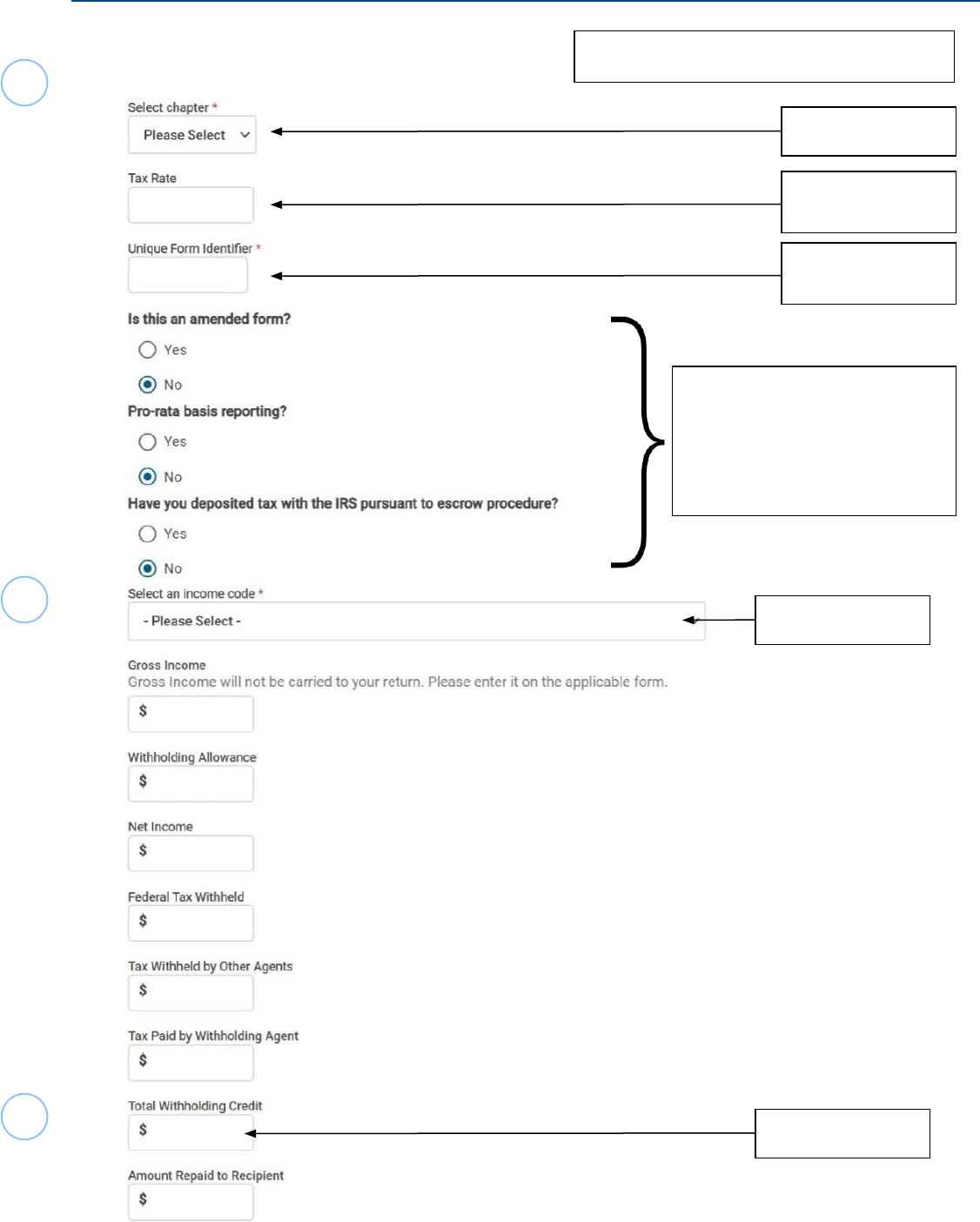
Form 1042-S Foreign Person’s U.S. Income Subject to Withholding
Box 3
Box 3b or 4b rate,
if listed
Listed above Box
3
Generally, Out-of-Scope.
(Amended Returns are
permitted for current year and
special circumstances based
on the site’s established
procedures.)
Box 1
Box 10
Corresponding Box from Form 1042-S

24
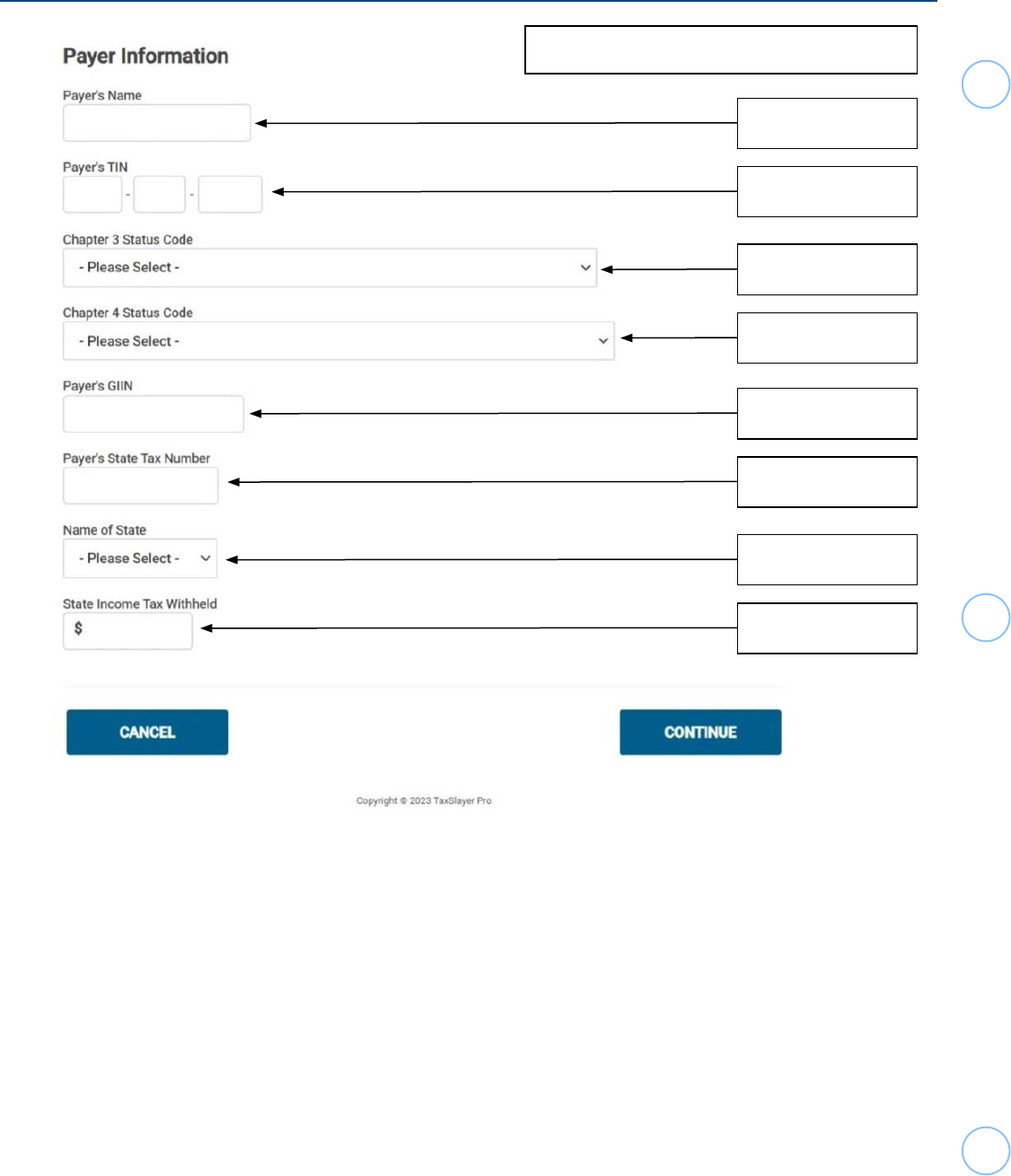
Form 1042-S Foreign Person’s U.S. Income Subject to Withholding
Box 12d
Box 12a
Box 12b
Box 12c
Box 12e
Box 12g
Box 12h
Box 12i
Box 12i
Corresponding Box from Form 1042-S
Box 13f
Box 13g
Box 13h
Box 13i
Box 13j
Box 13k

25
Form 1042-S Foreign Person’s U.S. Income Subject to Withholding
Box 14a
Box 14b
Corresponding Box from Form 1042-S
Box 15d
Box 15a
Box 15b
Box 15c
Box 15e
Box 15g
Box 15h
Box 15i
Box 15i
Box 15i
26
Form 1042-S Foreign Person’s U.S. Income Subject to Withholding
Box 16a
Box 16b
Box 16d
Box 16e
Corresponding Box from Form 1042-S
Box 16c
Box 17b
Box 17c
Box 17a

27
Form 1042-S
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service
Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding
Go to www.irs.gov/Form1042S for instructions and the latest information.
2023
UNIQUE FORM IDENTIFIER
AMENDED
AMENDMENT NO.
OMB No. 1545-0096
Copy A for
Internal Revenue Service
1 Income
code
2 Gross income
3 Chapter indicator. Enter “3” or “4”
3a Exemption code
3b Tax rate .
4a
Exemption code
4b Tax rate .
5 Withholding allowance
6 Net income
7a Federal tax withheld
7b Check if federal tax withheld was not deposited with the IRS because
escrow procedures were applied (see instructions) . . . . . .
7c Check if withholding occurred in subsequent year with respect to a
partnership interest . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 Tax withheld by other agents
9
Overwithheld tax repaid to recipient pursuant to adjustment procedures (see instructions)
( )
10 Total withholding credit (combine boxes 7a, 8, and 9)
11 Tax paid by withholding agent (amounts not withheld) (see instructions)
12a Withholding agent
’
s EIN
12b
Ch. 3 status code
12c
Ch. 4 status code
12d Withholding agent
’
s name
12e Withholding agent
’
s Global Intermediary Identification Number (GIIN)
12f Country code 12g Foreign tax identification number, if any
12h Address (number and street)
12i City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code
13a Recipient
’
s name 13b Recipient
’
s country code
13c
Address (number and street)
13d City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code
13e Recipient’s U.S. TIN, if any
13f Ch. 3 status code
13g Ch. 4 status code
13h Recipient’s GIIN
13i
Recipient
’
s
foreign tax identification
number, if any
13j
LOB code
13k Recipient
’
s account number
13l Recipient
’
s date of birth (YYYYMMDD)
14a
Primary Withholding Agent
’
s
Name (if applicable)
14b Primary Withholding Agent
’
s EIN
15 Check if pro-rata basis reporting
15a
Intermediary or flow-through entity’s EIN, if any
15b
Ch. 3 status code
15c
Ch. 4 status code
15d
Intermediary or flow-through entity’s name
15e
Intermediary or flow-through entity’s GIIN
15f Country code 15g Foreign tax identification number, if any
15h Address (number and street)
15i City or town, state or province, country, ZIP or foreign postal code
16a Payer
’
s name 16b Payer
’
s TIN
16c Payer
’
s GIIN
16d
Ch. 3 status code
16e
Ch. 4 status code
17a State income tax withheld 17b Payer
’
s state tax no. 17c Name of state
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see instructions.
Cat. No. 11386R
Form 1042-S (2023)

28
Filing Status
Generally, nonresident aliens must use either the Single or the Married Filing Separately (Married
Nonresident Alien) filing status. (Only residents of Canada, Mexico, Republic of Korea (S. Korea), and
India may qualify for the Qualifying Surviving Spouse, if applicable.) The married nonresident alien status
can be used whether their spouse is present in the U.S. or not.
Head of household filing status cannot be used if the taxpayer was a nonresident alien during any part
of a year.
Nonresidents who are married to U.S. Citizens or resident aliens can make an election to file a joint return
for tax purposes on Form 1040 and file as Married Filing Jointly. (Preparation of the required attached
statement outlined in Publication 519 is Out of Scope.) If both married taxpayers are nonresident aliens,
they CANNOT file as Married Filing Jointly, they must file as Married Filing Separately.
STATE RETURNS: Check with the state income tax authorities regarding the correct filing status that
applies to any state return being prepared.
Exemption Personal/Dependent Issues
The personal and/or dependency exemption deduction for 2023 is $0 through 2025.
Nonresidents from the following countries may be able to claim their children as dependents. Everyone
claimed on the return must have either a Social Security number (SSN) or a valid Individual Taxpayer
Identification Number (ITIN).
Canada Mexico India South Korea
The exemption amount for 2023 is $0. For India and South Korea, refer to Publication 519 for additional
information..
Standard or Itemized Deduction
Standard Deduction - Nonresident aliens are generally not eligible for the standard deduction. For those
eligible (India Treaty), they must use the amount for the single or married filing separately filing status
being used (if legally blind, or over 65, see Publication 501).
Generally, the standard deduction amount for single or married filing separately for 2023 is $13,850.
Itemized Deductions - The Tax Reform Act of 2017 limits the dollar amount of state and local income
taxes that are allowable to $10,000. Miscellaneous Itemized deductions for employee business expenses,
tax preparation fees, etc. have been eliminated. Casualty Losses are now only permitted for Presidentially
Declared Disaster areas (and remain Out of Scope).
The amount you can deduct for contributions made to U.S. qualified charitable organizations is generally
limited to no more than 60% of your AGI. Your deduction may be further limited to 50%, 30%, or 20% of
your AGI, depending on the type of property you give and the type of organization you give it to. Refer to
the Instructions for Form 1040-NR for more information. All other allowable itemized deductions on Form
1040-NR remain unchanged.

29
Wage Calculation Worksheet
Since some employers do not issue the correct reporting documents to international students and
scholars, the following formula will help you to accurately compute the amount of wages to
be shown on
the income tax return.
Wages from Form W-2, box 1 (if any)
Add: Code 19 or 20 income from Form,
1042-S, box 2 (if any) +
To t a l
W-2 and 1042-S
Subtract: Code 19 or 20 treaty benefit
Equals: Wages to be reported on
-
Form 1040-NR, line 8 =
Tax Credits and Nonresident Aliens
Tax credits are allowed to nonresident aliens only if they receive effectively connected income. Generally,
nonresident alien students and scholars will not qualify for tax credits.
Nonresident aliens cannot elect to be treated as resident aliens in order to claim these credits.
(See exception for Married Filing Jointly in the Filing Status section of this publication, and certain
treaty provisions for students from Barbados, Hungary, and Jamaica, as well as trainees from
Jamaica. These exception elections and treaty provisions are both Out of Scope.)
Child Tax Credit — Nonresident aliens may be able to claim the child tax credit if all of the following
conditions are met:
• The child is a U.S. citizen, national, or resident alien who resides with the taxpayer, and
• The child is a son, daughter, adopted child, grandchild, stepchild, or foster child, and
• The child was under age 17 at the end of the year, and
• The child qualifies as their dependent.
• The child MUST have a valid Social Security number
Child and Dependent Care Credit — Nonresident aliens may be able to claim the Child and Dependent
Care Credit if all of the following conditions are met:
• Pay a qualifying caregiver to care for a dependent under the age of 13, or a disabled dependent (any age), or
a disabled spouse, so the taxpayer and spouse (if applicable) can work or look for work.
• Pay for care provided during the hours when a student or scholar was working (or looking for work) rather
than attending classes or studying.
• Not claim an expense for the credit in an amount exceeding earned income from the United States.
• Generally, married persons must file a joint return to claim the credit. If your filing status is married filing
separately and all of the following apply, you are considered unmarried for purposes of claiming the credit
on Form 2441.
You lived apart from your spouse during the last 6 months of tax year.
Your home was the qualifying person’s main home for more than half of the tax year.
You paid more than half of the cost of keeping up that home for the tax year.
Credit for Other Dependents — If the taxpayer has a qualifying dependent who does not meet some of
the requirements for the Child Tax Credit, they may qualify for the Credit for Other Dependents. The child
must reside in the U.S. with the taxpayer and have a valid SSN or ITIN. (See Publication 17, Your Federal
Income Tax (For Individuals) for details.)
Earned Income Credit — If the taxpayer is a nonresident for any part of the year, the earned income
credit is not available.
Education Credits — If the taxpayer is a nonresident alien for any part of the year, they generally can’t
claim the educational credits, such as the American Opportunity Credit and Lifetime Learning Credit.

30
Foreign Tax Credit — This credit will usually not be available to nonresident alien students and scholars.
Their foreign-source income is usually not reported on their U.S. income tax return.
Advanced Premium Tax Credit — (As with many other credits, married taxpayers filing separately do
NOT qualify for the Premium Tax Credit.) If the taxpayer obtained insurance through the Marketplace
and received an Advanced Premium Tax Credit (listed on Form 1095-A, Health Insurance Marketplace
Statement), this must be reported. The following instructions should be followed to report the credit and, if
necessary, repay it:
1.
In TaxSlayer’s Health Insurance section, answer “Yes” to having received a Form 1095-A,
and “Yes” to “Are
you required to repay all of the APTC?” This will cause the software to add the repayment required into the
tax liability.
2. Complete and attach Form 8962, Premium Tax Credit (PTC), to calculate the repayment amount.
Social Security and Medicare Taxes
Generally, a nonresident alien temporarily admitted in the United States as a student is not permitted to work
for a wage or salary or to engage in business while in the United States. However, if a student is granted
permission to work, Social Security and Medicare taxes are not withheld from their pay. This exclusion
ONLY applies to the student, not their spouse or dependents under accompaniment statuses. Individuals in
F-2 or J-2 immigration status are never exempt from FICA (Social Security and Medicare Taxes)
If Social Security or Medicare taxes are withheld from pay that is not subject to these taxes, contact the
employer who withheld the taxes in error for a refund. The employer would also be eligible for a refund of
their portion of the erroneously withheld taxes.
If that employer does not refund the withheld taxes, file Form 843, Claim for Refund and Request for
Abatement and attach supporting documentation for reimbursement.
See Publication 519, Chapter 8, Paying Tax Through Withholding or Estimated Tax, for a list of items to
attach as supporting documentation. Mail Form 843 (with attachments, including Form 8316, Information
Regarding Request for Refund of Social Security Tax) to the following address:
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service Center
Ogden, UT 84201-0038
What Form(s) to File
Form 8843: If any of the following applies: If you are a nonresident alien, excluding days of presence in
the United States for purposes of the substantial presence test because you:
• were an exempt individual (temporarily in the United States as a teacher or trainee in “J” or “Q”
immigration status; temporarily in the United States as a student in an “F”, “J”, “M”, or “Q” immigration
status; or you were a professional athlete competing in a charitable event, or
• were unable to leave the United States as planned because of a medical condition or problem.
• meet the qualifications of Rev. Proc. 2020-20 for COVID-19 travel restrictions.
Even if the student or scholar had no income, they still must file Form 8843 by the 15th day of the 6th
month after your tax year ends (June 15th) and file one for each family member who is in the U.S. also
excluding days of presence. (The test for residency must be applied separately for each individual under
the above immigration statuses).
If Canadian students are exempt individuals and do not have a visa, use the information from their work
authorization papers to complete Form 8843. Form 1040-NR: For all filing of income and/or treaty benefits.

31
When to File
Taxpayers will have until April 15, 2024 to file their 2023 return.
If you did not receive wages subject to U.S. income tax withholding, or are filing a standalone Form 8843,
file your return by the 15th day of the 6th month after the tax year ends (June 15th).
When the regular due date for filing falls on a Saturday, Sunday, or legal holiday, file by the next
business day.
Extensions of time to file - If you cannot file your return by the regular due date, file Form 4868,
Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return.
For the 2023 calendar year, the due date is April 15, 2024 making any extension due October 15, 2024
(December 16, 2024 if the due date of your return is June 17, 2024).
You must file the extension by the regular due date of your tax return and pay any tax due with the
request for extension.
Amended Returns - If you later have changes in your income, deductions, or credits after you file your
return, file Form 1040-X, Amended U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. Also use Form 1040-X if you
should have filed Form 1040 instead of Form 1040-NR or vice versa.
If you amend Form 1040-NR or filed a previous Form 1040-X, attach the most recently filed form to the
correct Form 1040-X. Print “Amended” across the top of the attached corrected forms or schedules.
If you are claiming a refund, the amended return must be filed within 3 years from the date the return was
filed or within 2 years from the time the tax was paid, whichever is later.
A tax return filed before the final due date is considered to have been filed on the due date.
Amending the Form 1040-NR using Form 1040-X is handled differently from other amended
returns. Please see Form 1040-X instructions for the proper procedures.
www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/i1040x.pdf
Where to File
For those returns that cannot be efiled, the returns must be mailed. Tax returns cannot be faxed or
emailed to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
For Form 1040-NR,
if enclosing a payment, mail to:
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service
P.O. Box 1303
Charlotte, NC 28201-1303
USA
Forms 8843 and 1040-NR
must be mailed to:
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service
Austin, TX 73301-0215
USA

32
Payment Options
Some students and scholars owe money with their tax return. This is usually due to insufficient withholding
from wages.
Nonresidents have the same payment options as citizens; they can:
• Pay the entire balance by the due date for the return, by direct pay, card or digital wallet, or an IRS Online Account
• Put the balance on a credit card (fees apply)
• Ask for an extension of time to pay or an installment agreement (fees may apply)
Explain to taxpayers that:
• Interest, and any applicable penalties, will continue to accrue until they pay the full amount due
• They should not send cash through the mail; personal checks, cashiers’ checks, and money orders are accepted
Source Documents
You may see many types of income documents when you are assisting international students andscholars.
The following list may help you in identifying the documents you may see.
Form 1042-S, Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding - Many students and scholars
will receive this form if they have income and/or a scholarship that is subject to treaty benefits.
Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement - Most students and scholars are allowed to work. If they earn more
than the amount exempted by their treaty, the excess should be reported on the W-2. When students and
scholars work off campus, they often receive a W-2 for the full amount they earned. That is why it is important
to use the Wage Calculation Worksheet in this guide.
Form 1098-T, Tuition Statement - Academic institutions issue Form 1098-T to students who paid tuition
during the tax year. This form helps the students calculate the educational credits. Since nonresident aliens
usually cannot claim the educational credits, the form is not part of their tax return.
Form 1099-INT, Interest Income - Many banks and savings institutions issue the 1099-INT to nonresident
alien and scholars. Since most nonresident student and scholars do not need to report their interest income,
the form is not part of their tax return. To avoid receiving a Form 1099-INT, file Form W-8 BEN with the bank
or financial institution.
Form 1099-NEC, Nonemployee Compensation - Sometimes a nonresident alien student or scholar will give
you a 1099-NEC. There are several complicated issues involved when this happens. These returns are Out
of Scope for the VITA/TCE Foreign Student and Scholar program and must be referred to a professional tax
preparer.
Forms 1095-A, Health Insurance Marketplace Statement - If the taxpayer has a F1095-A that indicates an
Advanced Premium Tax Credit was allowed, the taxpayer will need to complete Form 8962, calculating the
proper credit amount and repaying any excess advances, as necessary.

33
Additional Resources
• Link & Learn Taxes for Foreign Student Course
• Forms 1040-NR, U.S. Nonresident Alien Income Tax Return
• Form 843, Claim for Refund and Request for Abatement
• Form 8233, Exemption from Withholding on Compensation for Independent (& Certain Dependent)
Personal Service of a Nonresident Alien Individual
• Form 8316, Information Regarding Request for Refund of Social Security Tax Erroneously Withheld
on Wages Received by a Nonresident Alien on an F, J, or M Type
• Form 8843, Statement for Exempt Individuals and Individuals With a Medical Condition
• Form 13614-NR, Nonresident Alien Intake and Interview Sheet
• Instructions for Schedule 8812, Credits for Qualifying Children and Other Dependents
• Publication 519, U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens
• Publication 597, Information on the United States-Canada Income Tax Treaty
• Publication 901, U.S. Tax Treaties
• Publication 1915, Understanding your IRS Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN)
• Publication 970, Tax Benefits for Education
• Publication 4152, Electronic Toolkit for Nonresident Alien VITA/TCE Sites
• Publication 4756,
Foreign Student and Scholar Volunteer Tax Return Preparation PowerPoint presentation
• Publication 4757, Individual Taxpayer Identification Number PowerPoint presentation
• Publication 5087-FS, VITA/TCE Foreign Student and Scholar Resource Guide

34
General Summary of U.S. Immigration Terms
Alien – An individual who is not a U.S. citizen or U.S. national. For Income tax purposes, aliens are
classified as Residents or Nonresidents.
Bona Fide Resident — An individual who is established in a foreign country or countries for an
uninterrupted period which includes an entire year that extends into the current tax year.
Dual Status — Aliens who are both Residents and Nonresidents of the U.S. within the same tax year.
Exempt Individual — Aliens who, because of the terms of their immigration status, are not considered to
be “present in the United States” for purposes of the substantial presence test.
Exempt Status — A visa status that provides for a defined period of time in which the days an alien is
physically present in the U.S. are not counted for purposes of the substantial presence test.
Expatriation Tax — An additional tax that may apply to U.S. citizens who have renounced their
citizenship and long-term residents who have ended their U.S. resident status for federal tax purposes.
Different rules apply according to the date upon which you expatriated.
Green Card, (F I-551, U.S. Permanent Resident Card) —An alien registration card issued by U.S.
Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) giving an individual the privilege, according to the
immigration laws, of residing permanently in the U.S. as an immigrant.
Taxpayer Identification Number — A unique number used by individuals and other tax entities to file tax
forms with the IRS.
Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) — A tax processing number issued by the Internal
Revenue Service. It is a nine-digit number that always begins with the number 9. ITINs are for federal
tax reporting only, and are not intended to serve any other purpose. IRS issues ITINs to help individuals
comply with the U.S. tax laws, and to provide a means to efficiently process and account for tax returns
and payments for those not eligible for Social Security Numbers (SSNs). An ITIN does not authorize work
in the U.S. or provide eligibility for Social Security benefits or the Earned Income Tax Credit.
ITINs issued will expire if unused on a federal tax return for 3 consecutive years. If expired, you
must reapply for a new number, if needed.
Nonresident Alien — An alien who is temporarily residing in the U.S., a resident alien who has
abandoned permanent residence in the United States, or an alien who has never been in the U.S. A
nonresident alien is an individual who has not passed the lawful permanent residency test (Green Card
test) or the substantial presence test for the calendar year.
Resident Alien — Aliens admitted to the U.S. under permanent immigration visas are generally resident
aliens and meet the substantial presence test or lawful permanent residency test. (green card test).
Substantial Presence Test — A rule applied in determining if an alien is a U.S. Resident for tax
purposes. Generally, an individual meets the substantial presence test if the individual was in the U.S. for
at least 31 days during the current calendar year and was present in the U.S. for at least 183 days during
the current year and the two preceding calendar years.
For purposes of the substantial presence test, an individual does not count days of temporary
presence in the United States under certain visas.)
Social Security Number (SSN) – A nine-digit number issued by the Social Security Administration to
U.S. citizens and aliens permitted to work in the United States.
Treaty Benefits – Provisions of a tax treaty that allow for various items of tax relief or responsibility not
provided for under general tax laws.

35
Nonimmigrant Visas – Allows a nonimmigrant to enter the United States in one of several different
categories, which correspond to the reason the nonimmigrant was allowed to enter the U.S.
Nonimmigrant – An alien who has been granted the right to reside temporarily in the United States.
Immigrant –
An alien who has been granted the right to reside permanently in the United States and work without
restrictions. Also known as a Lawful Permanent Resident (LPR), they are eventually issued a “green
card”.
Passport – An official government document that certifies one’s identity and citizenship and permits a citizen to
travel abroad.
U.S. National – An individual who, although not a U.S. citizen, owes his/her allegiance to the United States.
U.S. nationals include individuals born in American Samoa or the Commonwealth of Northern Mariana Islands.
U.S. Citizen – An individual born in the United States, Puerto Rico, Guam or the U.S. Virgin Islands, or an
individual whose parent is a U.S. citizen, or a former alien who has been naturalized as a U.S. citizen.
Job Aid- Filers without an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number
(ITIN) or a Social Security Number (SSN)
If Then
Filers without an ITIN or a
SSN that only need to file a
Form 8843
Complete Form 8843 leaving the “Your U.S. taxpayer identification number” box blank
Filers without an ITIN
(ineligible for SSN) and
in addition to the Form
8843 needs to file a Form
1040-NR
The following are the most common ways to apply for an ITIN using Form W-7, Application for IRS
Individual Taxpayer Identification Number
• In person at IRS Taxpayer Assistance Center, www.irs.gov search box
“Local IRS office” to see list of locations, services provided, and whether an
appointment is required.
• By mail, follow instructions for the W-7
• Through an Acceptance Agent or Certifying Acceptance Agent (CAA),
listing at www.irs.gov search box “Acceptance Agent Program”
• Through the Student and Exchange Visitor Program (SEVP) for more
information www.irs.gov search box “SEVP”
Filers eligible for a SSN
Must apply for SSN at www.ssa.gov/ or a local Social Security Office using Form SS-5, Application
for Social Security Card
Cannot apply for an ITIN
ITIN has expired ITINs, will be deactivated if not used on at least one federal income tax return for three consecutive
years. The taxpayer will be notified of the deactivation.
Must re-apply for ITIN, if needed, see instructions above

36
NOTES

Quality Review Check List
After reviewing the tax return and verifying that it reects correct tax law application to the
information provided by the taxpayer, notate “QR Complete” with initials on the F13614-NR.
A 100% Quality Review is required on all tax returns using
a completed Form 13614-NR, source documents, and this Check List.
A signed Form 14446, Virtual VITA/TCE Taxpayer Consent, was received before preparing a virtual return.
Return was accurately determined to be within the scope of the VITA/TCE Foreign Student and Scholar
program.
Volunteer return preparer and quality reviewer had proper certification levels for the return.
Residency status for tax purposes was properly determined
Taxpayer’s identity, address, and phone numbers were verified. (Govt. issued photo ID)
Names, SSN or ITINs and dates of birth of taxpayer (and spouse and dependents, if from Canada, Mexico,
India, or South Korea) match supporting documents
NOTE: ITINs will expire if not used on a federal income tax return for three consecutive years.
Filing status is correctly determined (single or the proper married status, etc.).
All allowable dependents properly listed for eligible credits, etc. (Canada, Mexico, India and South Korea)
Dependents’ identification numbers and names listed correctly
Income items correctly transferred from Form W-2, Form 1042-S, and Form 1099 (amounts paid, name,
address, income codes, EIN, etc. properly listed)
Is all income reported? Including taxable amounts not reported on an income statement or from the payer
i
ncluding, but not limited to all gambling and lottery winnings, prizes and awards, rents, royalties, stock sales, etc.
Itemized deduction section line completed accurately or Standard deduction (students from India only) is correct.
All allowable credits are correctly entered.
Withholding shown on Forms W-2, 1042-S, 1099, and estimated tax reported correctly.
All calculations are correct.
If a treaty benefit was claimed, the proper treaty article was listed in the proper section(s).
Has a Form 8843 completed, as necessary, for the taxpayer and any accompanying spouse and children.
Overpayment (or balance due) computed correctly
Direct Debit or Direct Deposit information was entered correctly, as applicable.
Advise the taxpayer of their responsibility to provide correct information in the preparation of the return prior to signing
.
Advise the taxpayer of where to sign the return: Form 8843, Form 1040-NR, or Form 8879, IRS e-file
Signature Authorization. [If a child has to file a tax return or Form 8843, but can’t sign the form, the child’s
parent, guardian, or another legally responsible person must sign the child’s name, followed by the words
“By (Your signature) Parent for Minor Child”.]
If filing by paper, all Forms W-2 and 1042-S, as well as schedules and forms, are attached to the return.
Advised of proper mailing address.
SIDN and Site Name are properly listed on the return.

Your online resource for volunteer and taxpayer assistance
Partner and Volunteer Resource Center
www.irs.gov/Individuals/Partner-and-Volunteer-Resource-Center
• What’s Hot!
• Partner & Volunteer Quality
• Partner & Volunteer Tax Preparation
Scope & Products
Quality and Tax Alerts for IRS Volunteer Programs
www.irs.gov/Individuals/Quality-and-Tax-Alerts-for-IRS-Volunteer-Programs
• Quality Site Requirement Alerts (QSRA)
• Volunteer Tax Alerts (VTA)
Volunteer Training Resources
www.irs.gov/Individuals/Volunteer-Training-Resources
Outreach Connection
www.irs.gov/Outreach-Connection
Interactive Tax Assistant (ITA)
www.irs.gov/help/ita
Tax Information for Individuals
www.irs.gov/Individuals
Identity Theft Protections
Get Help Now
eBooks
Want to view our training products on your mobile or tablet devices? Click here to
access our eBooks: www.irs.gov/Individuals/Site-Coordinator-Corner
IRS2Go Mobile App
Another device to use for additional information is IRS2Go. Click here to download
IRS2Go mobile app:
www.irs.gov/newsroom/irs2goapp
and much more!
Your direct link to tax information 24/7: www.irs.gov
Tools
• Sign into Your Account
• Get Your Transcript
• Where’s My Refund
File your taxes
• Special deadlines for taxpayers living
overseas and some disaster victims
• What to do if you haven’t filed your
tax return
• Filing past due returns
• What you need to know before you file
• Learn about electronic filing options,
including IRS Free File
• Get free tax help from volunteers
• Find tips for choosing a tax professional
• Avoid these common errors
• Avoid penalty for underpayment of
estimated tax
IRS.gov.gov
After you le your taxes
• Pay taxes you owe, including
estimated taxes
• Not getting a refund? Learn how to pay
taxes if you owe
• Unexpectedly owe taxes? You may
need to adjust your withholding
• Refund you received different than
expected?
• Understanding your IRS notice or letter
• Need to correct your taxes? Amend a
tax return
• Check the status of your amended return
• Partner & Volunteer Links to
Outreach Products
• Partner & Volunteer Online Tools
• Partner & Volunteer Tips
